69
CHAPTER 3 INTERRUPTS
3.5.2 Occurrence and Release of Hardware Interrupt
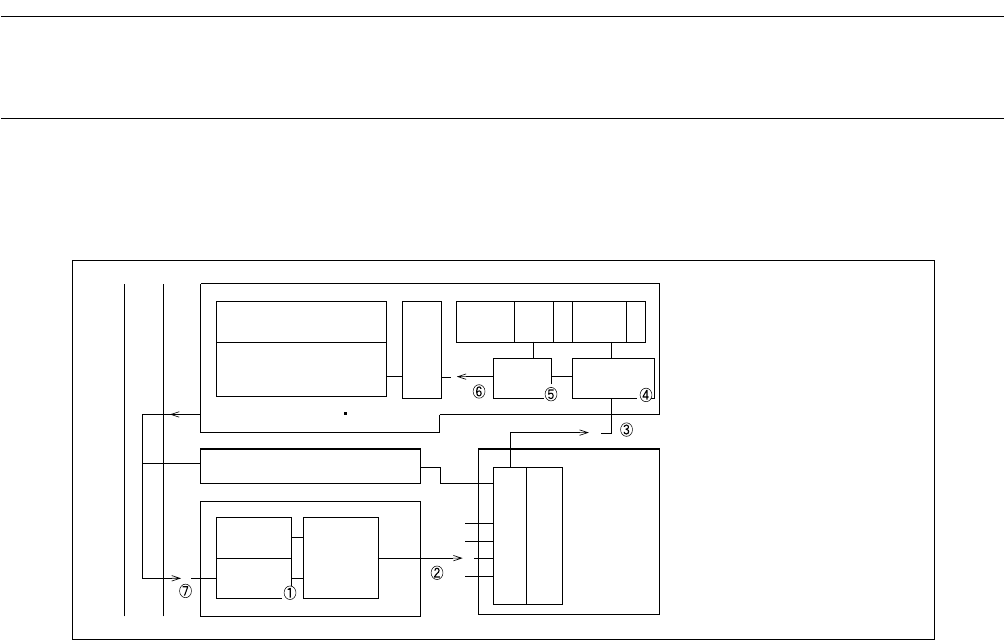
Figure 3.5-1 shows the processing flow from occurrence of a hardware interrupt to
release of the interrupt request in an interrupt processing program.
■ Occurrence and Release of Hardware Interrupt
Figure 3.5-1 Occurrence and Release of Hardware Interrupt
1. An interrupt cause occurs in a peripheral.
2. The interrupt enable bit in the peripheral is referred. If interrupts are enabled, the peripheral issues an
interrupt request to the interrupt controller.
3. Upon reception of the interrupt request, the interrupt controller determines the priority levels of
simultaneously requested interrupts. Then, the interrupt controller transfers the interrupt level of the
corresponding interrupt to the CPU.
4. The CPU compares the interrupt level requested by the interrupt controller with the ILM bit of the
processor status register.
5. If the comparison shows that the requested level is higher than the current interrupt processing level, the
I flag value of the same processor status register is checked.
6. If the check in step 5. shows that the I flag indicates interrupt enable status, the requested level is
written to the ILM bit. Interrupt processing is performed as soon as the currently executing instruction
is completed, then control is transferred to the interrupt processing routine.
7. When the interrupt cause of step 1. is cleared by software in the user interrupt processing routine, the
interrupt request is completed.
IR
PS I ILM
AND
F
2
MC-16LX CPU
F
2
MC-16LX bus
Register file
Micro code
Check
Comparator
Peripheral
Enable FF
Factor FF
Interrupt
controller
PS : Processor status
I : Interrupt enable flag
ILM : Interrupt level mask register
IR : Instruction register
•
•
•
Level comparator
Interrupt level IL


















