584
APPENDIX
●
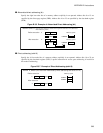
I/O direct bit addressing (io:bp)
Specify bits in physical addresses 000000
H
to 0000FF
H
explicitly. Bit positions are indicated by ":bp",
where the larger number indicates the most significant bit (MSB) and the lower number indicates the least
significant bit (LSB).
Figure B.3-8 Example of I/O Direct Bit Addressing (io:bp)
●
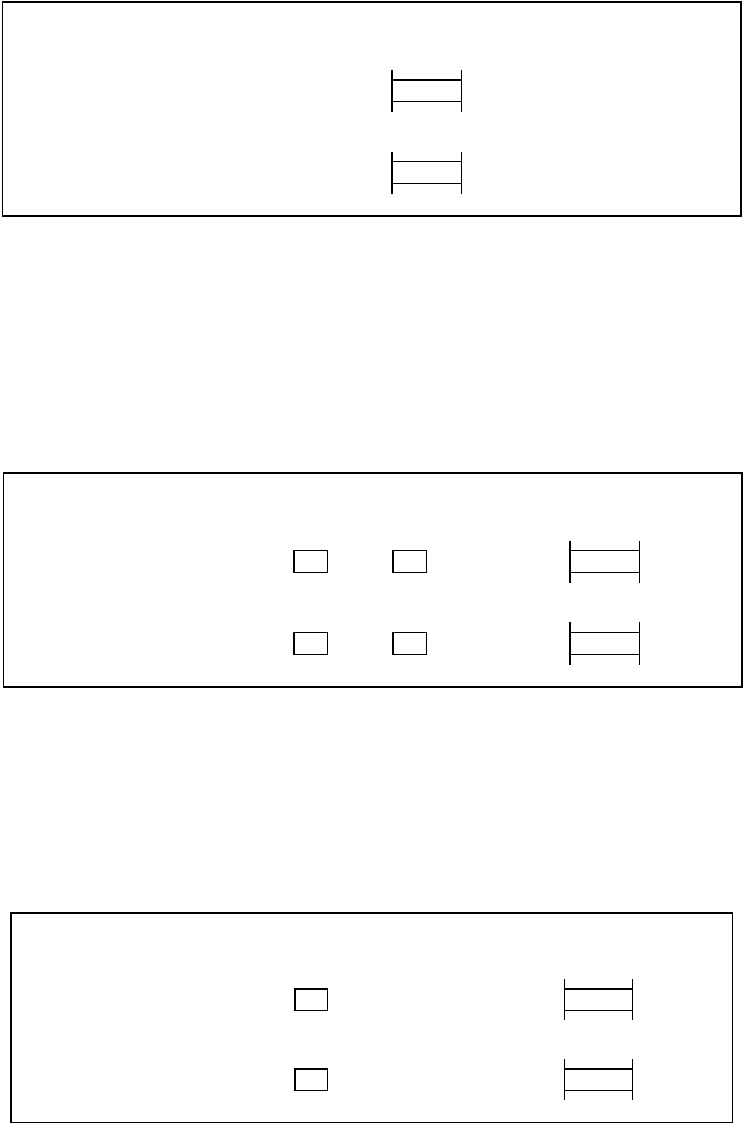
Abbreviated direct bit addressing (dir:bp)
Specify the eight low-order bits of a memory address explicitly in an operand. Address bits 8 to 15 are
specified by the direct page register (DPR). Address bits 16 to 23 are specified by the data bank register
(DTB). Bit positions are indicated by ":bp", where the larger number indicates the most significant bit
(MSB) and the lower number indicates the least significant bit (LSB).
Figure B.3-9 Example of Abbreviated Direct Bit Addressing (dir:bp)
●
Direct bit addressing (addr16:bp)
Specify arbitrary bits in 64K bytes explicitly. Address bits 16 to 23 are specified by the data bank register
(DTB). Bit positions are indicated by ":bp", where the larger number indicates the most significant bit
(MSB) and the lower number indicates the least significant bit (LSB).
Figure B.3-10 Example of Direct Bit Addressing (addr16:bp)
0 0
0 1
0000C1H
0000C1H
Before execution
After execution
SETB I:0C1H:0
Memory space
(This instruction sets bits by I/O direct bit addressing.)
SETB S:10H:0
5 5DTB
5 5
0 0
0 1
DTB
6 6DPR
6 6
DPR
556610H
556610H
Before execution
After execution
Memory space
Memory space
(This instruction sets bits by abbreviated direct bit addressing.)
SETB 2222H:0
5 5DTB
5 5
0 0
0 1
DTB
552222H
552222H
Before execution
After execution
Memory space
Memory space
(This instruction sets bits by direct bit addressing.)