56
CHAPTER 3 INTERRUPTS
3.1 Outline of Interrupts
The F
2
MC-16LX has interrupt functions that terminate the currently executing
processing and transfer control to another specified program when a specified event
occurs. There are four types of interrupt functions:
• Hardware interrupt: Interrupt processing due to an internal resource event
• Software interrupt: Interrupt processing due to a software event occurrence instruction
• Extended intelligent I/O service (EI
2
OS): Transfer processing due to an internal
resource event
• Exception: Termination due to an operation exception
■ Hardware Interrupts
A hardware interrupt is activated by an interrupt request from an internal resource. A hardware interrupt
request occurs when both the interrupt request flag and the interrupt enable flag in an internal resource are
set. Therefore, an internal resource must have an interrupt request flag and interrupt enable flag to issue a
hardware interrupt request.
●
Specifying an interrupt level
An interrupt level can be specified for the hardware interrupt. To specify an interrupt level, use
the level setting bits (IL0, IL1, and IL2) of the interrupt controller.
●
Masking a hardware interrupt request
A hardware interrupt request can be masked by using the I flag of the processor status register
(PS) in the CPU and the ILM bits (IL0, IL1, and IL2). When an unmasked interrupt request
occurs, the CPU saves 12 bytes of data that consists of registers PS, PC, PCB, DTB, ADB, DPR,
and A in the memory area indicated by the SSB and SSP registers.
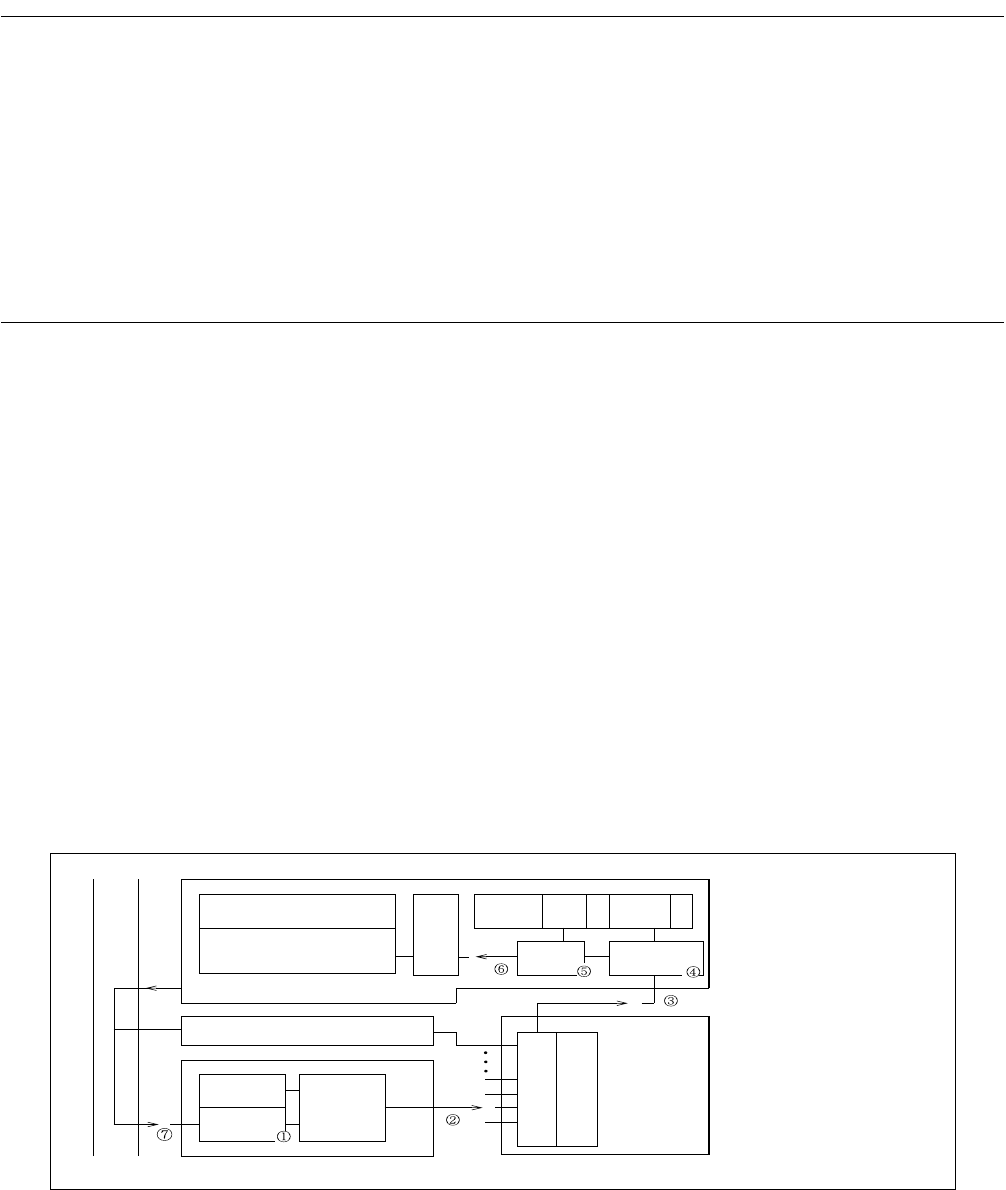
Figure 3.1-1 Overview of Hardware Interrupts
IR
PS I ILM
AND
F
2
MC-16LX CPU
F
2
MC-16LX
Enable FF
Factor FF
Register file
Micro code
Check
Comparator
bus
Peripheral
Interrupt
controller
PS : Processor status
I : Interrupt enable flag
ILM : Interrupt level mask register
IR : Instruction register
Interrupt level IL
Level comparator