57
CHAPTER 3 INTERRUPTS
■ Software Interrupts
Interrupts requested by executing the INT instruction are software interrupts. An interrupt request by the
INT instruction does not have an interrupt request or enable flag. An interrupt request is issued always by
executing the INT instruction.
No interrupt level is assigned to the INT instruction. Therefore, ILM is not updated when the INT
instruction is used. Instead, the I flag is cleared and the continuing interrupt requests are suspended.
Figure 3.1-2 Overview of Software Interrupts
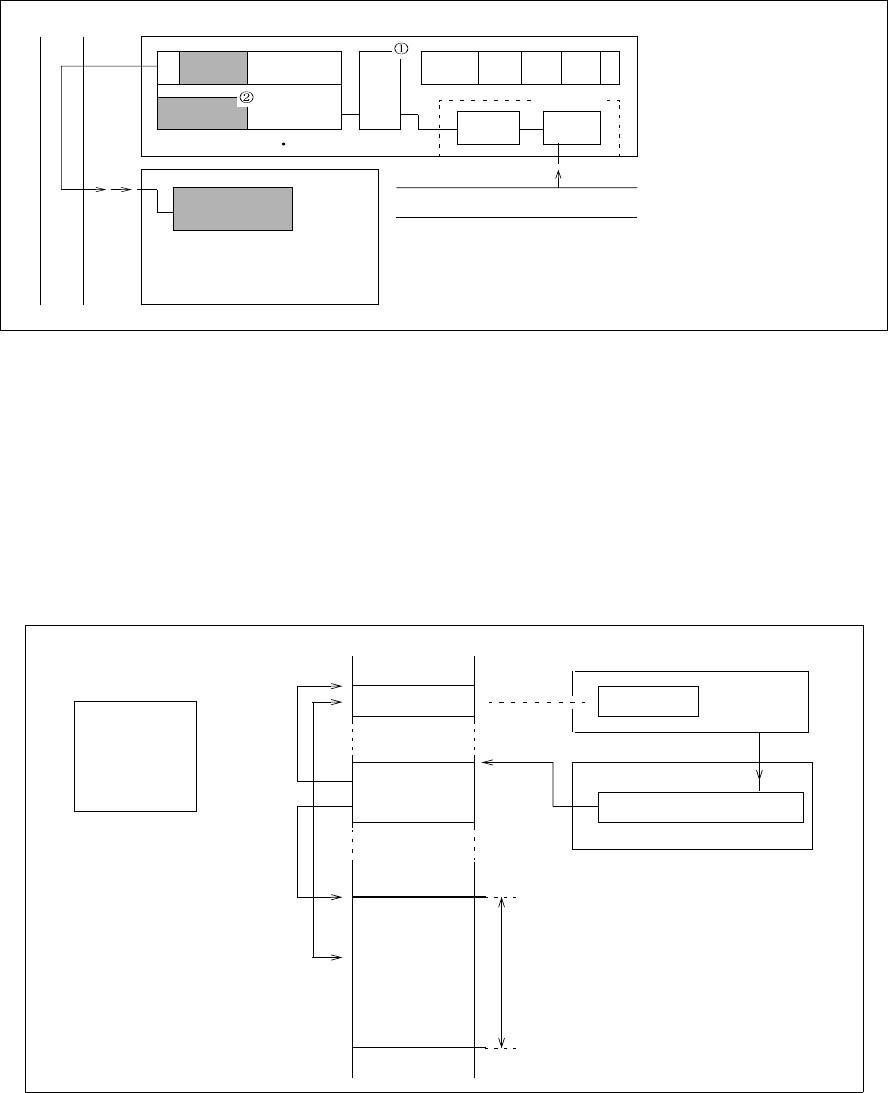
■ Extended Intelligent I/O Service (EI
2
OS)
The extended intelligent I/O service automatically transfers data between an internal resource and memory.
This processing is traditionally performed by an interrupt processing program, but the EI
2
OS enables data
to be transferred in a manner similar to a DMA (direct memory access) operation.
To activate the extended intelligent I/O service function from an internal resource, the interrupt control
register (ICR) of the interrupt controller must have an extended intelligent I/O service enable flag (ISE).
The extended intelligent I/O service is started when an interrupt request occurs with 1 specified in the ISE
flag. To generate a normal interrupt using a hardware interrupt request, set the ISE flag to 0.
Figure 3.1-3 Overview of the Extended Intelligent I/O Service (EI
2
OS)
RAM
IR
PS I S
F
2
MC-16LX
CPU
F
2
MC-16LX
PS : Processor status
I : Interrupt enable flag
ILM : Interrupt level mask register
IR : Instruction register
B unit : Bus interface unit
B unit
Instruction bus
Register
file
Micro
code
Queue
Fetch
Save
bus
CPU
IOA
BAP
ISD
ICS
DCT
Peripheral
I/O register
I/O register
Interrupt request
Buffer
Memory space
(3)
(3)
(4)
(2)
(1)
Interrupt control register
Interrupt controller
(1) I/O requests transfer.
(2) Interrupt controller selects descriptor.
(3) Transfer source and destination are read
from descriptor.
(4) Data is transferred between I/O and
memory.