454
CHAPTER 21 CAN CONTROLLER
21.4.2 Function of Control Status Register (CSR)
The operating status of the register’s each bit is confirmed by following;
• Setting "0" or "1"
• Function control by writing
•Read
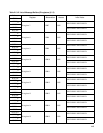
■ Control Status Register (CSR-lower)
Table 21.4-1 Function of Each Bit of the Control Status Register (CSR:L)
Bit Name Function
bit7 TOE:
Transmit output
enable bit
This bit switches from a general-purpose I/O port to a transmit pin TX.
When setting to 0: Functions as general-purpose I/O port.
When setting to 1: Functions as transmit pin TX.
bit6 to
bit3
Undefined bits When reading: Value is undefined.
When writing: No effect
bit2 NIE:
Node status
transition interrupt
output enable bit
This bit controls a node status transition interrupt generation (CSR: NT = 1) when a node
status is transferred.
When setting to 0: Interrupt generation is disabled.
When setting to 1: Interrupt generation is enabled.
bit1 Reserved:
Reserved bit
This bit is always set to 0.
When reading: The value is always 0.
bit0 HALT:
Bus operation halt
bit
This bit controls the bus halt. The halt state of the bus can be checked by reading this bit.
Writing to this bit:
0: Cancels bus halt
1: Halt bus
Reading from this bit:
0: Bus operation not in stop state
1: Bus operation in stop state
Note: After ensuring that 1 is written to this bit, write 0 to this bit if the node status is Bus
Off.
Example program:
switch ( IO_CANCT1.CSR.bit.NS )
{
case 0 : /* error active */
break;
case 1 : /* warning */
break;
case 2 : /* error passive */
break;
default : /* bus off */
for ( i=0; ( i <= 500 ) || ( IO_CANCT1.CSR.bit.HALT == 0); i++);
IO_CANCT1.CSR.word = 0x0084; /* HALT = 0 */
break;
}
*: The variable "i" is used for fail-safe.
For detail information, see "21.4.4 Notes on Using Bus Operation Stop Bit (HALT = 1)".