Intel386™ EX EMBEDDED PROCESSOR USER’S MANUAL
10-6
10.2.1 Mode 0 – Interrupt on Terminal Count
This mode allows you to generate a rising edge on a counter’s OUTn signal. Initializing a counter
for mode 0 drives the counter’s OUTn signal low and initiates counting. When the counter reach-
es terminal count, OUTn is driven high. At this point, the counter rolls over and continues count-
ing with OUTn high. OUTn stays high and the counter keeps counting down and rolling over until
a new count is written or you reprogram the counter. You can write a new count to the counter at
any time to drive OUTn low and start a new counting sequence. Writing a new control word re-
programs the counter.
Mode 0’s basic operation is outlined below and shown in Figure 10-2.
1. After a control word write, OUTn is driven low.
2. On the CLKINn pulse following a count write, the count is loaded.
3. On each succeeding CLKINn pulse, the count is decremented.
4. When the count reaches terminal count, OUTn is driven high.
NOTE
Writing a count of N causes a rising edge on OUTn in N + 1 CLKINn pulses
(provided GATEn remains high and count was written before the rising edge of
CLKINn).
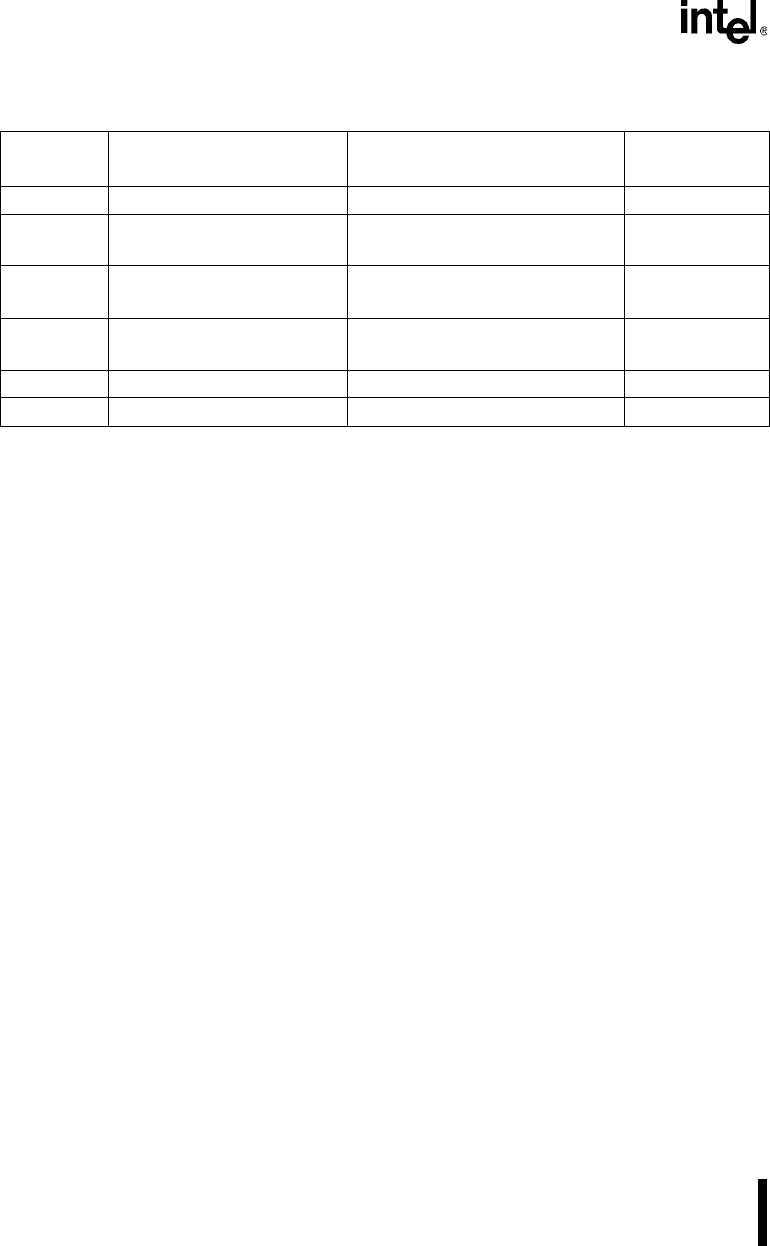
Table 10-3. Operations Caused by GATE
n
Operating
Modes
Low or Falling Rising High
0 Disables counting — Enables counting
1 — 1) Initiates counting
2) Resets OUT
n
after next CLKIN
n
—
2 1) Disables counting
2) Sets OUT
n
immediately high
Initiates counting Enables counting
3 1) Disables counting
2) Sets OUT
n
immediately high
Initiates counting Enables counting
4 Disables counting — Enables counting
5 — Initiates counting —


















