14-19
CHIP-SELECT UNIT
14.4.4 Chip-select Mask Registers
The Mask Register of each chip-select region is used to prevent bits from being compared with
the starting address, thus masking them from the comparison. This masking allows you to specify
the size of the region being defined. The mask should be set such that it masks the lower address
bits being compared, up to the size that you would like the block to be.
Write a channel’s 15-bit mask to the chip-select mask registers. Also, use the chip-select low
mask register to enable the channel and to mask the channel’s SMM address bit. When the chan-
nel’s SMM address bit is masked, the CSU activates the channel even if the channel is operating
in SMM.
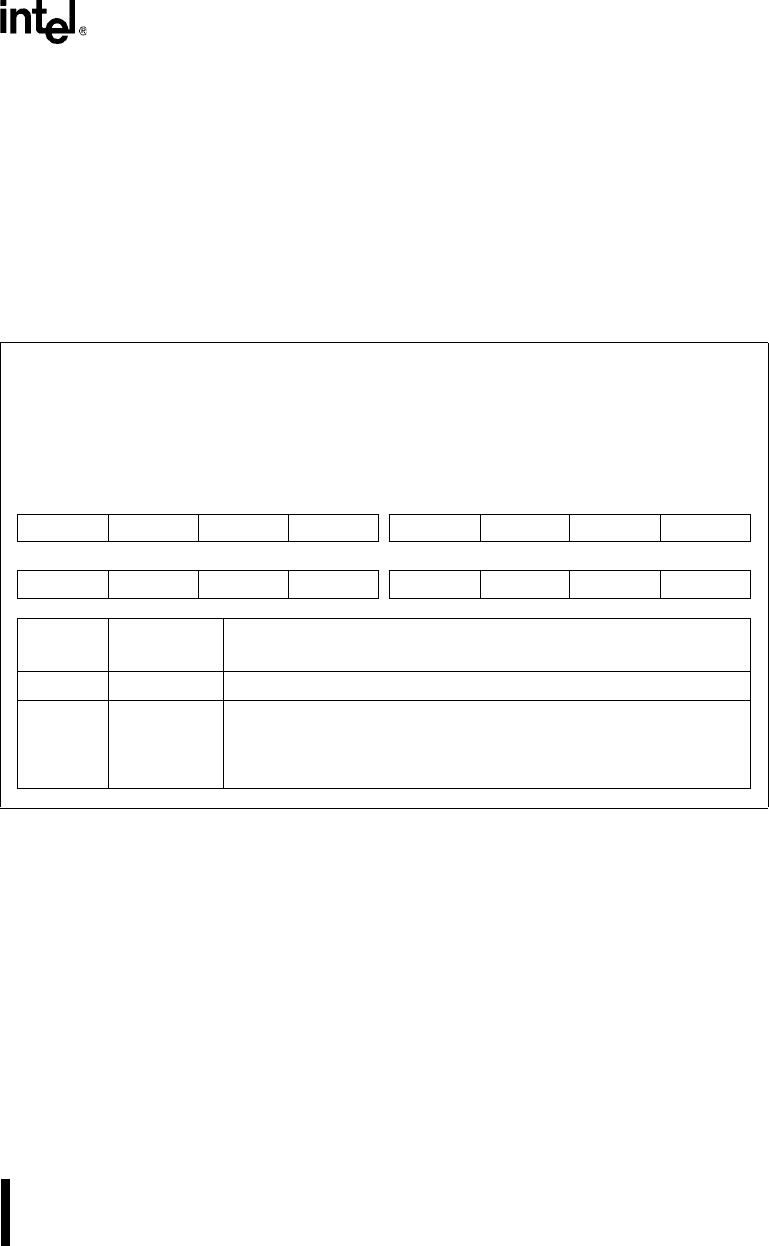
Figure 14-8. Chip-select High Mask Registers (CS
n
MSKH, UCSMSKH)
Chip-select High Mask
CS
n
MSKH (
n
= 0–6), UCSMSKH
(read/write)
Expanded Addr:
ISA Addr:
Reset State:
F406H, F40EH
F416H, F41EH
F426H, F42EH
F436H, F43EH
—
0000H (CS
n
MSKH)
FFFFH (UCSMSKH)
15 8
———— ——CM15CM14
7 0
CM13 CM12 CM11 CM10 CM9 CM8 CM7 CM6
Bit
Number
Bit
Mnemonic
Function
15–10 — Reserved; for compatibility with future devices, write zeros to these bits.
9–0 CM15:6 Mask Value Upper Bits:
Defines the upper 10 bits of the channel’s 15-bit mask. The mask bits
CM15:6 and the address bits CA15:6 form a masked address that is
compared to memory address bits A25:16 or I/O address bits A15:6.


















