12-49
DMA CONTROLLER
12.3.15 Interrupt Status Register (DMAIS)
DMAIS indicates which source activated the DMA interrupt request signal (channel 0 transfer
complete, channel 1 transfer complete, channel 0 chaining, or channel 1 chaining).
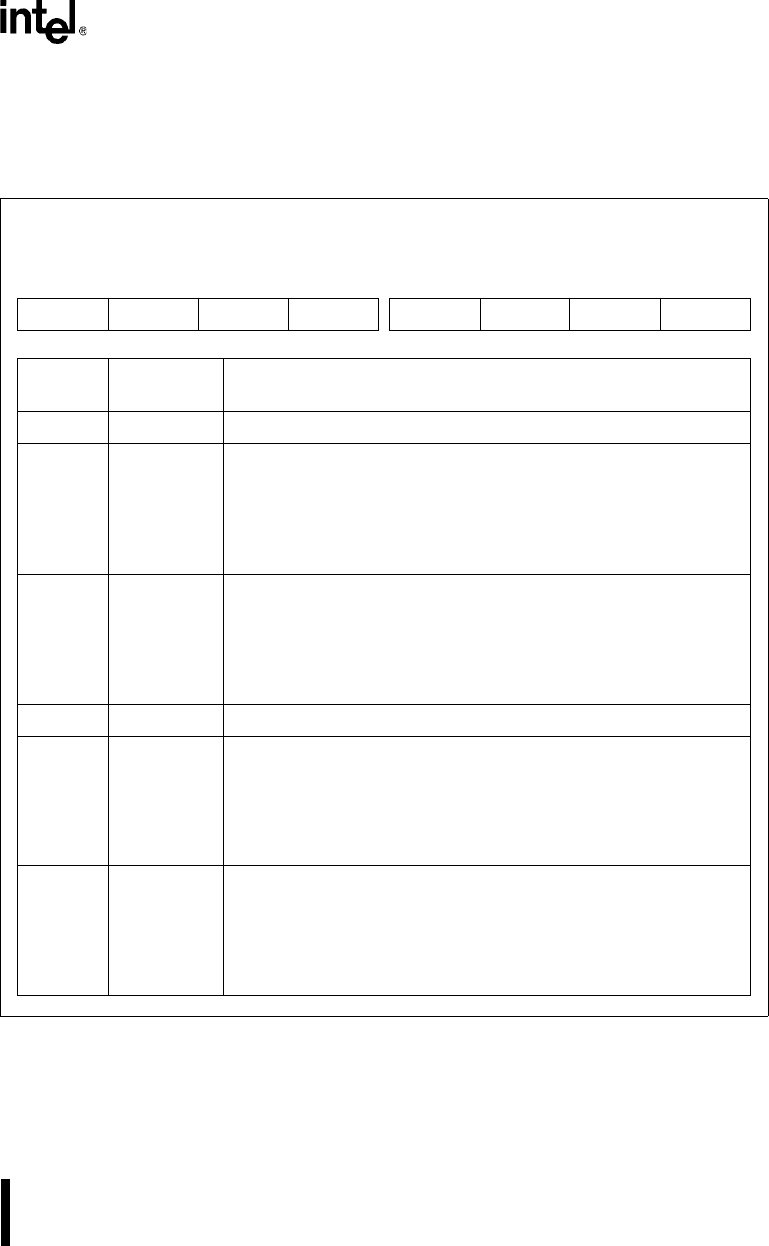
Figure 12-34. DMA Interrupt Status Register (DMAIS)
DMA Interrupt Status
DMAIS
(read only)
Expanded Addr:
ISA Addr:
Reset State:
F019H
—
00H
7 0
——
TC1 TC0
——
CI1 CI0
Bit
Number
Bit
Mnemonic
Function
7–6
—
Reserved. These bits are undefined.
5 TC1 Transfer Complete 1:
When set, this bit indicates that channel 1 has completed a buffer
transfer (either its byte count expired or it received an EOP# input). This
bit is set only if bit 1 of the interrupt enable register is set. Reading the
DMA status register (DMASTS) clears this bit.
Note: In chaining mode, this bit becomes a don’t care.
4 TC0 Transfer Complete 0:
When set, this bit indicates that channel 0 has completed a buffer
transfer (either its byte count expired or it received an EOP# input). This
bit is set only if bit 0 of the interrupt enable register is set. Reading the
DMA status register (DMASTS) clears this bit.
Note: In chaining mode, this bit becomes a don’t care.
3–2
—
Reserved. These bits are undefined.
1 CI1 Chaining Interrupt 1:
When set, this bit indicates that new requester and target addresses and
a new byte count should be written to channel 1. This bit is cleared when
new transfer information is written to the channel. (Writing to the most-
significant byte of the target address clears this bit.)
Note: Outside chaining mode, this bit becomes a don’t care.
0 CI0 Chaining Interrupt 0:
When set, this bit indicates that new requester and target addresses and
a new byte count should be written to channel 0. This bit is cleared when
new transfer information is written to the channel. (Writing to the most-
significant byte of the target address clears this bit.)
Note: Outside chaining mode, this bit becomes a don’t care.


















