Intel386™ EX EMBEDDED MICROPROCESSOR USER’S MANUAL
13-16
13.3 REGISTER DEFINITIONS
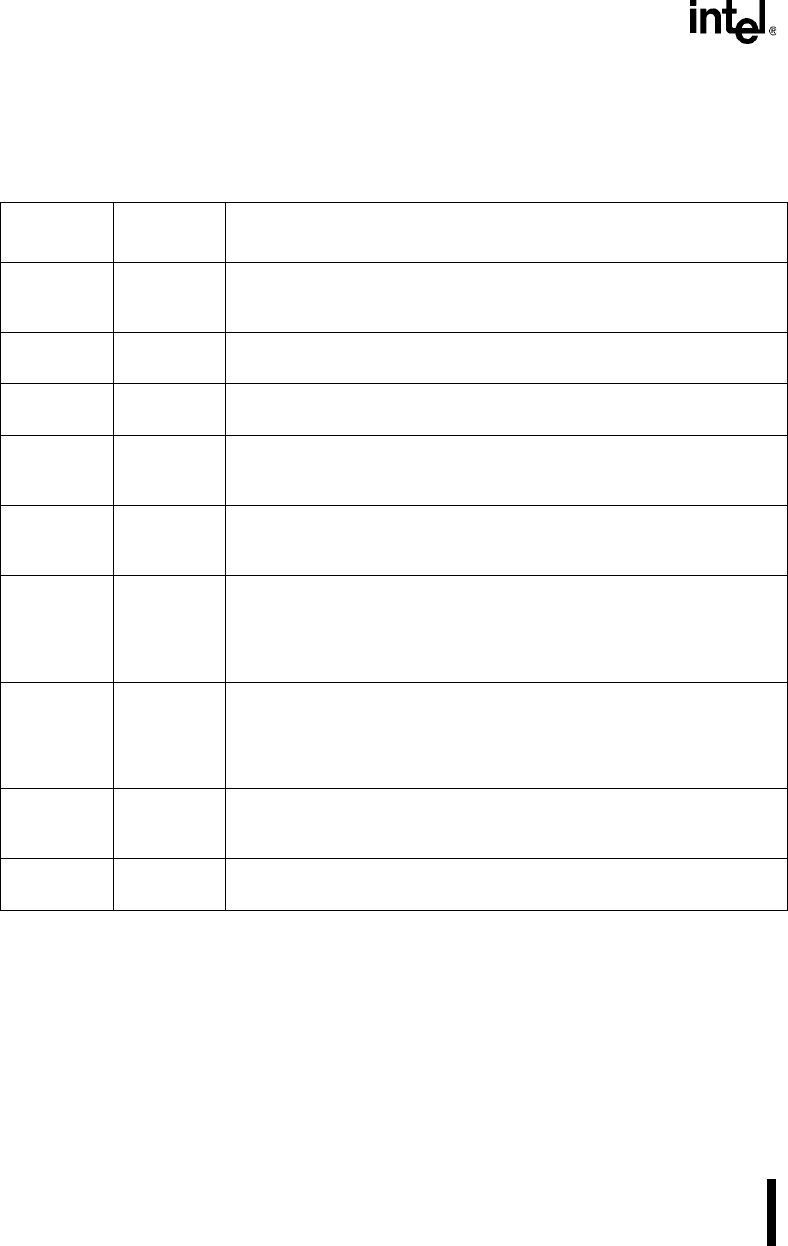
Table 13-3 list the registers associated with the SSIO and the following sections contain bit de-
scriptions for each register.
Table 13-3. SSIO Registers
Register
Expanded
Address
Function
PINCFG
(read/write)
F826H Pin Configuration:
Connects the serial receive clock signal (SRXCLK) and the transmit serial
data signal (SSIOTX) to the package pin.
SIOCFG
(read/write)
F836H SIO and SSIO Configuration:
Selects the baud-rate generator’s clock source, SERCLK or PSCLK.
CLKPRS
(read/write)
F804H Clock Prescale:
Controls the frequency of PSCLK.
SSIOBAUD
(read/write)
F484H SSIO Baud-rate Control:
Enables the baud-rate generator and determines its baud rate. In master
mode, the transmitter and receiver are clocked by the baud-rate generator.
SSIOCTR
(read only)
F48AH SSIO Baud-rate Count Down:
Indicates whether the baud-rate generator is enabled and reflects the current
value of the baud-rate down-counter.
SSIOCON1
(read/write)
F486H SSIO Control 1:
Enables the transmitter and receiver, indicates when the transmit buffer is
empty and the receive buffer is full. Enables or disables the transmitter or
receiver interrupts. SSIOCON1 also indicates two error conditions: the
transmit underrun and receiver overflow.
SSIOCON2
(read/write)
F488H SSIO Control 2:
Selects whether the transmitter and receiver are in master or slave mode. In
master mode, the baud-rate generator clocks the transmitter or receiver. In
slave mode, an external master clocks the transmitter or receiver. Also
controls the enabling of the Automatic Transmit mode.
SSIOTBUF
(read/write)
F480H SSIO Transmit Buffer:
Holds the 16-bit data word to transmit. Data is transmitted most-significant bit
first.
SSIORBUF
(read only)
F482H SSIO Receive Buffer:
Holds the 16-bit data word received. Data is received most-significant bit first.


















