11-13
ASYNCHRONOUS SERIAL I/O UNIT
11.2.6 SIO Interrupt and DMA Sources
11.2.6.1 SIO Interrupt Sources
Each SIO channel has four status signals: receiver line status, receiver buffer full, transmit buffer
empty, and modem status. An overrun error, parity error, framing error, or break condition can
activate the receiver line status signal. When the receiver transfers data from its shift register to
its buffer, it activates the receive buffer full signal. When the transmitter transfers data from its
transmit buffer to its transmit shift register, it activates the transmit buffer empty signal. A change
on any of the modem control input signals activates the modem status signal. When the modem
signals are connected internally either through the configuration register or the diagnostic mode,
changes of state still activate the modem status signal. For these cases, however, the signal values
are controlled by register bits rather than by external input signals.
Each of the four status signals can be used as an interrupt request source for the SIOINTn signal.
The Interrupt Enable register (IER) is used to enable any or all of the status signals as interrupt
sources. When an SIOINTn occurs the IP# bit (bit 0) of the Interrupt ID register (IIRn) is cleared
and the interrupt handler must determine which of the status signals caused the interrupt by read-
ing bits 1 and 2 of the IIRn register (Table 11-4). When more than one status signal is enabled as
an interrupt source and two or more are active at the same time then the source of the interrupt is
based on a fixed priority scheme (Table 11-4).
11.2.6.2 SIO DMA sources
The transmit and receive channel on each SIO is supported by both DMA channels. The receiver
buffer full and transmit buffer empty signals of the line status register are brought out as
RBFDMAn, and TXEDMAn. The TXEDMAn signal is connected directly to the multiplexers
controlling the source of DREQn for each of the two DMA channels. The RBFDMAn signal is
also connected to the DREQn muxes, but it is qualified by the LSR error conditions so that the
DMA request is blocked if an error has occurred in the reception of a character. This prevents the
DMA from transferring a character from the SIO with an error.
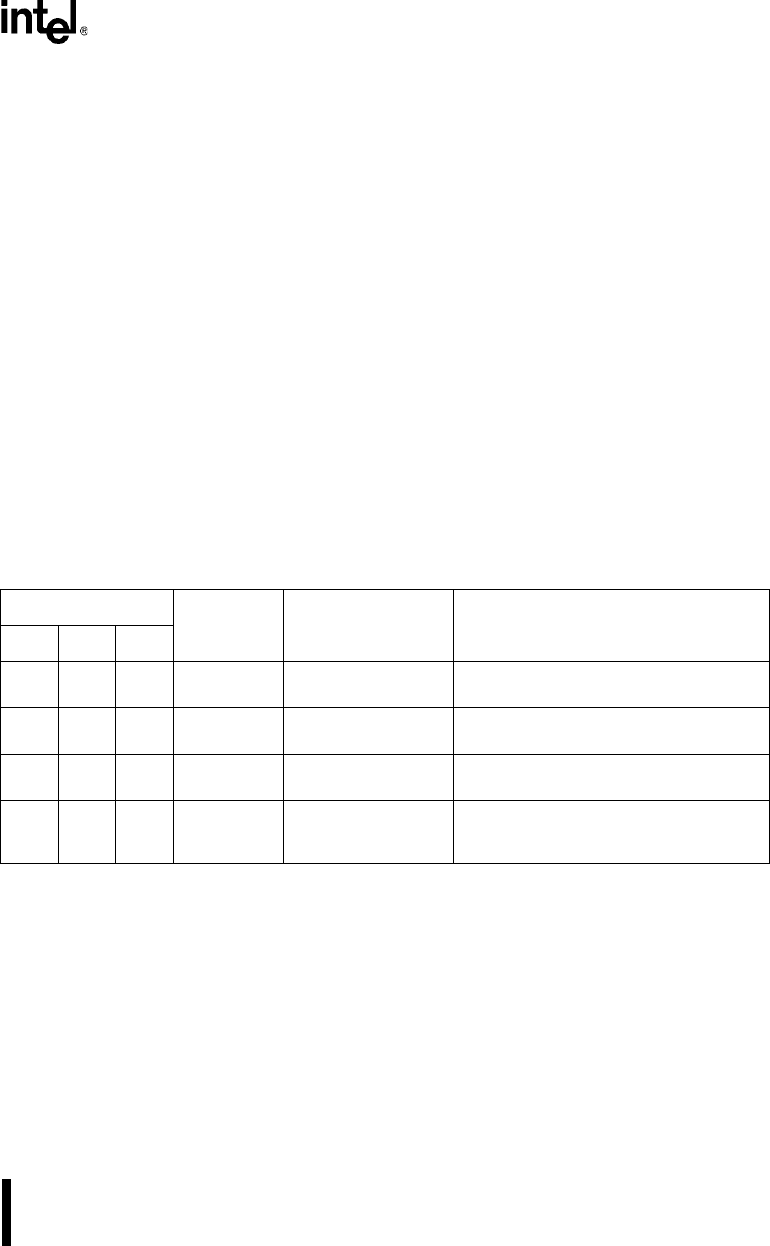
Table 11-4. Status Signal Priorities and Sources
Interrupt ID Register
Priority Status Signal Activated By
Bit 2Bit 1Bit 0
11 0
1 (Highest) Receiver Line Status overrun error, parity error, framing error, or
break condition
100
2 Receive Buffer Full the receiver transferring data from its shift
register to its buffer
010
3 Transmit Buffer Empty the transmitter transmitting data from its
transmit buffer to its transmit shift register
000
4 (Lowest) Modem Status a change on any of the modem control
input signals (CTS
n
#, DCD
n
#, DSR
n
#, and
RI
n
#


















