Intel386™ EX EMBEDDED MICROPROCESSOR USER’S MANUAL
12-34
NOTE
The value you write to the byte count register must be one less than the
number of bytes to be transferred. To transfer one byte, write zero to the byte
count register (byte count = number of bytes
– 1). To transfer one word, write
one (byte) to the byte count register (byte count = [number of words X 2]
– 1).
12.3.4 Overflow Enable Register (DMAOVFE)
Use DMAOVFE to specify whether all 26 bits or only the lower 16 bits of the target and requester
addresses are incremented or decremented during buffer transfers and to determine whether all
24 bits of the byte count or only the lower 16 bits of the byte count are decremented during buffer
transfers. A byte count configured for 16-bit decrementing expires when it is decremented from
0000H to 0FFFFH.
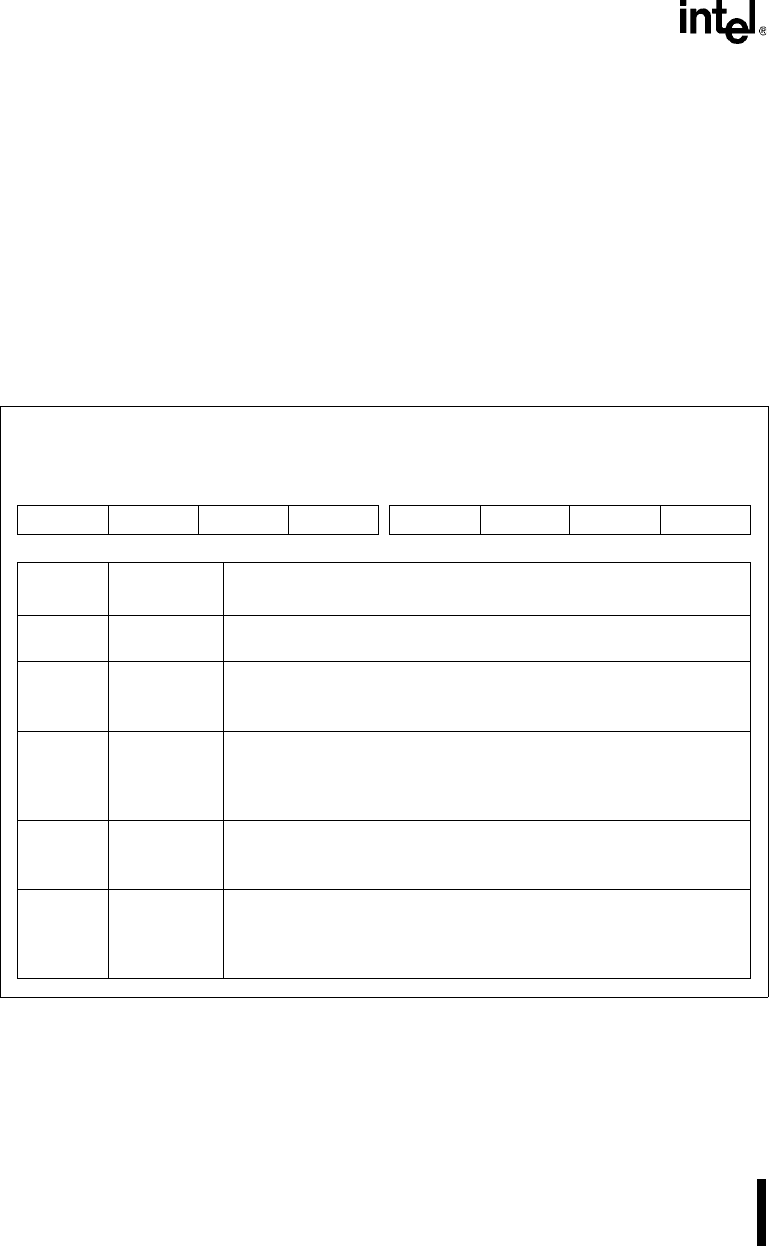
Figure 12-21. DMA Overflow Enable Register (DMAOVFE)
DMA Overflow Enable
DMAOVFE
(read/write)
Expanded Addr:
ISA Addr:
Reset State:
F01DH
—
0AH
7 0
— — — — ROV1 TOV1 ROV0 TOV0
Bit
Number
Bit
Mnemonic
Function
7–4 — Reserved. These bits are undefined; for compatibility with future devices,
do not modify these bits.
3 ROV1 Channel 1 Requester Overflow Enable:
0 = lowest 16 bits of requester address increment/decrement
1 = all bits of requester address increment/decrement
2 TOV1 Channel 1 Target & Byte Counter Overflow Enable:
0 = lowest 16 bits of target address and byte count
increment/decrement
1 = all bits of target address and byte count increment/decrement
1 ROV0 Channel 0 Requester Overflow Enable:
0 = lowest 16 bits of requester address increment/decrement
1 = all bits of requester address increment/decrement
0 TOV0 Channel 0 Target & Byte Counter Overflow Enable:
0 = lowest 16 bits of target address and byte count
increment/decrement
1 = all bits of target address and byte count increment/decrement


















