4-3
SYSTEM REGISTER ORGANIZATION
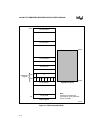
Figure 4-1. PC/AT I/O Address Space (10-bit Decode)
4.3 EXPANDED I/O ADDRESS SPACE
The Intel386 EX processor’s I/O address scheme is similar to that of the Extended Industry Stan-
dard Architecture (EISA) bus and the Enhanced - Industry Standard Architecture (E-ISA) bus.
Both standards maintain backward software compatibility with the ISA architecture. The ISA
Platform I/O (0-100H) is accessed with a 16-bit address decode and is located in the first 256 I/O
locations. The General Slot I/O that is typically used by add-in boards is repeated throughout the
64 Kbyte I/O address range due to their 10-bit only decode. This allows 63 of the 64 repetitions
of the first 256 address locations of every 1 Kbyte block to be allocated to specific slots. Each slot
is 4 Kbyte in size, allowing for a total of 16 slots. The partitioning is such that four groups of 256
address locations are assigned to each slot, for a total of 1024 specific address locations per slot.
General Slot I/O
Platform I/O (Reserved)
FC00H (63K)
FD00H
FFFFH (64K)
General Slot I/O
Platform I/O (Reserved)
0800H (2K)
0900H
0C00H (3K)
General Slot I/O
Platform I/O (Reserved)
0500H
General Slot I/O
Platform I/O (Reserved)
0100H (256)
0000H (0)
0400H (1K)
A2498-01