4-14 Vol. 3
PAGING
— If the P flag of a PTE is 1, bit 7 is reserved.
— If the P flag and the PS flag of a PDE are both 1, bit 12 is reserved.
(If CR4.PSE = 0, no bits are reserved with 32-bit paging.)
A reference using a linear address that is successfully translated to a physical
address is performed only if allowed by the access rights of the translation; see
Section 4.6.
Figure 4-4 gives a summary of the formats of CR3 and the paging-structure entries
with 32-bit paging. For the paging structure entries, it identifies separately the
format of entries that map pages, those that reference other paging structures, and
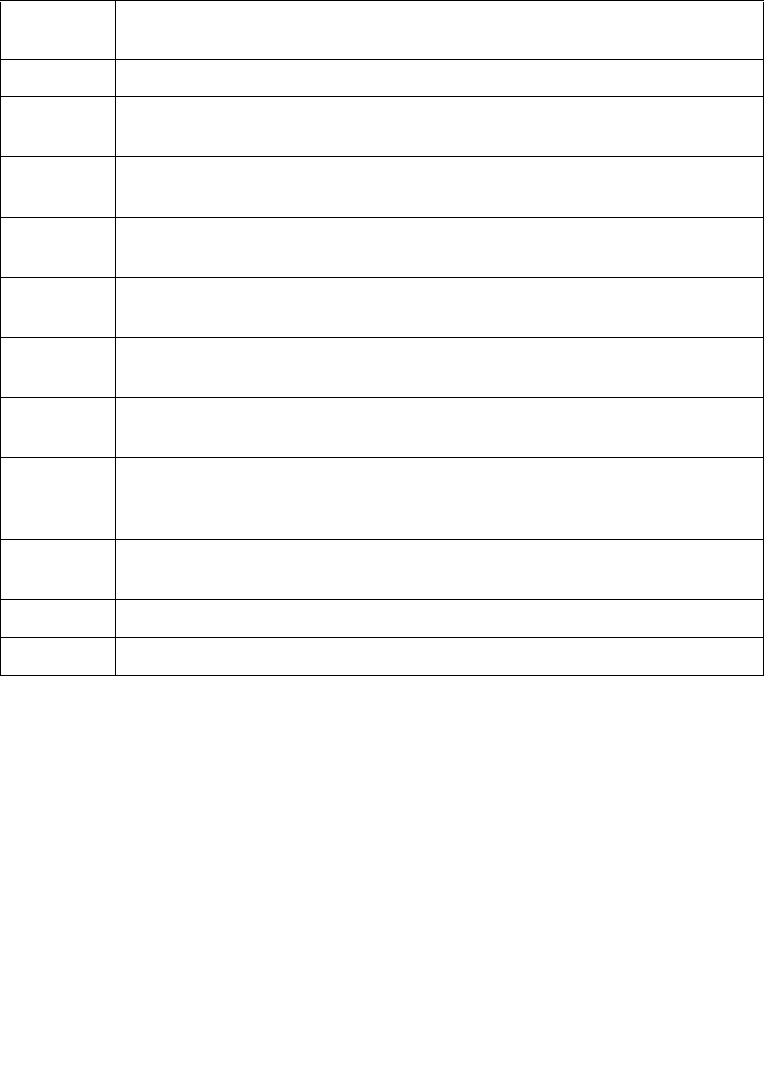
Table 4-6. Format of a 32-Bit Page-Table Entry that Maps a 4-KByte Page
Bit
Position(s)
Contents
0 (P) Present; must be 1 to map a 4-KByte page
1 (R/W) Read/write; if 0, writes may not be allowed to the 4-KByte page referenced by this
entry (depends on CPL and CR0.WP; see Section 4.6)
2 (U/S) User/supervisor; if 0, accesses with CPL=3 are not allowed to the 4-KByte page
referenced by this entry (see Section 4.6)
3 (PWT) Page-level write-through; indirectly determines the memory type used to access
the 4-KByte page referenced by this entry (see Section 4.9)
4 (PCD) Page-level cache disable; indirectly determines the memory type used to access
the 4-KByte page referenced by this entry (see Section 4.9)
5 (A) Accessed; indicates whether software has accessed the 4-KByte page referenced
by this entry (see Section 4.8)
6 (D) Dirty; indicates whether software has written to the 4-KByte page referenced by
this entry (see Section 4.8)
7 (PAT) If the PAT is supported, indirectly determines the memory type used to access the
4-KByte page referenced by this entry (see Section 4.9); otherwise, reserved
(must be 0)
1
8 (G) Global; if CR4.PGE = 1, determines whether the translation is global (see Section
4.10); ignored otherwise
11:9 Ignored
31:12 Physical address of the 4-KByte page referenced by this entry
NOTES:
1. See Section 4.1.4 for how to determine whether the PAT is supported.


















