Vol. 3 5-45
PROTECTION
5.13.3 Reserved Bit Checking
The processor enforces reserved bit checking in paging data structure entries. The
bits being checked varies with paging mode and may vary with the size of physical
address space.
Table 5-8 shows the reserved bits that are checked when the execute disable bit
capability is enabled (CR4.PAE = 1 and IA32_EFER.NXE = 1). Table 5-8 and Table
show the following paging modes:
• Non-PAE 4-KByte paging: 4-KByte-page only paging (CR4.PAE = 0,
CR4.PSE
= 0).
• PSE36: 4-KByte and 4-MByte pages (CR4.PAE = 0, CR4.PSE = 1).
• PAE: 4-KByte and 2-MByte pages (CR4.PAE = 1, CR4.PSE = X).
The reserved bit checking depends on the physical address size supported by the
implementation, which is reported in CPUID.80000008H. See the table note.
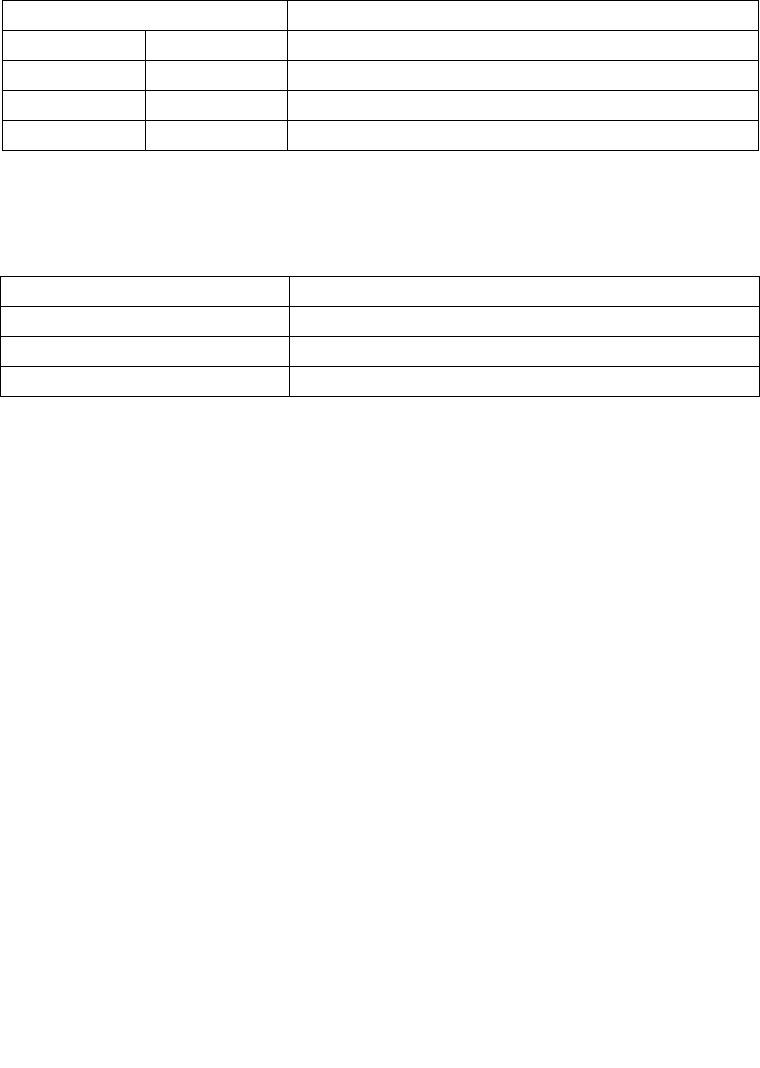
Table 5-6. Legacy PAE-Enabled 4-KByte Page Level Protection Matrix
with Execute-Disable Bit Capability
Execute Disable Bit Value (Bit 63) Valid Usage
PDE PTE
Bit 63 = 1 * Data
* Bit 63 = 1 Data
Bit 63 = 0 Bit 63 = 0 Data/Code
NOTE:
* Value not checked.
Table 5-7. Legacy PAE-Enabled 2-MByte Page Level Protection
with Execute-Disable Bit Capability
Execute Disable Bit Value (Bit 63) Valid Usage
PDE
Bit 63 = 1 Data
Bit 63 = 0 Data/Code


















