Vol. 3 9-55
PROCESSOR MANAGEMENT AND INITIALIZATION
}
//
// Compare the Update read to that written
//
If (Update read != Update written)
{
Display Diagnostic
exit
}
I ← I + (size of microcode update / 2048)
}
//
// Enable Update Loading, and inform user
//
Issue the Update Control function with Task = Enable.
9.11.8.3 Microcode Update Functions
Table 9-12 defines current Pentium 4, Intel Xeon, and P6 family processor microcode
update functions.
9.11.8.4 INT 15H-based Interface
Intel recommends that a BIOS interface be provided that allows additional microcode
updates to be added to system flash. The INT15H interface is the Intel-defined
method for doing this.
The program that calls this interface is responsible for providing three 64-kilobyte
RAM areas for BIOS use during calls to the read and write functions. These RAM
scratch pads can be used by the BIOS for any purpose, but only for the duration of
the function call. The calling routine places real mode segments pointing to the RAM
blocks in the CX, DX and SI registers. Calls to functions in this interface must be
made with a minimum of 32 kilobytes of stack available to the BIOS.
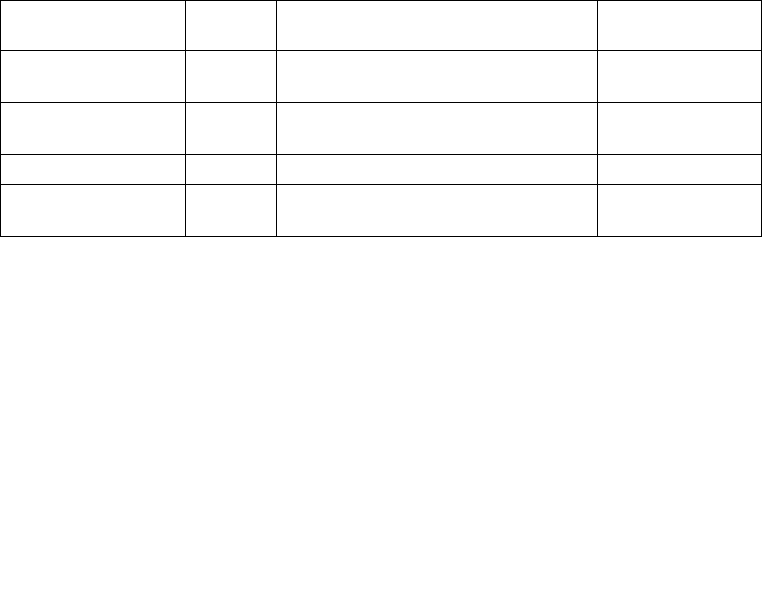
Table 9-12. Microcode Update Functions
Microcode Update
Function
Function
Number
Description Required/Optional
Presence test 00H Returns information about the
supported functions.
Required
Write update data 01H Writes one of the update data areas
(slots).
Required
Update control 02H Globally controls the loading of updates. Required
Read update data 03H Reads one of the update data areas
(slots).
Required


















