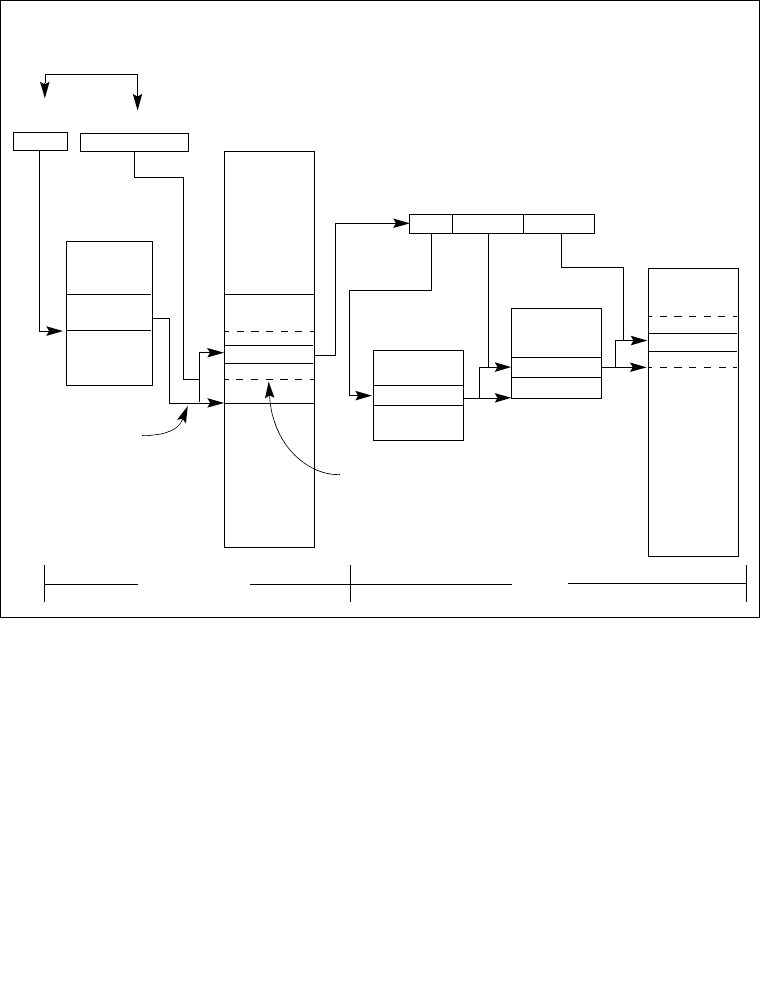
3-2 Vol. 3
PROTECTED-MODE MEMORY MANAGEMENT
segment, the segment type, and the location of the first byte of the segment in the
linear address space (called the base address of the segment). The offset part of the
logical address is added to the base address for the segment to locate a byte within
the segment. The base address plus the offset thus forms a linear address in the
processor’s linear address space.
If paging is not used, the linear address space of the processor is mapped directly
into the physical address space of processor. The physical address space is defined as
the range of addresses that the processor can generate on its address bus.
Because multitasking computing systems commonly define a linear address space
much larger than it is economically feasible to contain all at once in physical memory,
some method of “virtualizing” the linear address space is needed. This virtualization
of the linear address space is handled through the processor’s paging mechanism.
Paging supports a “virtual memory” environment where a large linear address space
is simulated with a small amount of physical memory (RAM and ROM) and some disk
Figure 3-1. Segmentation and Paging
Global Descriptor
Table (GDT)
Linear Address
Space
Segment
Segment
Descriptor
Offset
Logical Address
Segment
Base Address
Page
Phy. Addr.
Lin. Addr.
Segment
Selector
Dir
Table Offset
Linear Address
Page Table
Page Directory
Entry
Physical
Space
Entry
(or Far Pointer)
Paging
Segmentation
Address
Page


















