6-14 Vol. 3
INTERRUPT AND EXCEPTION HANDLING
6.11 IDT DESCRIPTORS
The IDT may contain any of three kinds of gate descriptors:
• Task-gate descriptor
• Interrupt-gate descriptor
• Trap-gate descriptor
Figure 6-2 shows the formats for the task-gate, interrupt-gate, and trap-gate
descriptors. The format of a task gate used in an IDT is the same as that of a task
gate used in the GDT or an LDT (see
Section 7.2.5, “Task-Gate Descriptor”). The task
gate contains the segment selector for a TSS for an exception and/or interrupt
handler task.
Interrupt and trap gates are very similar to call gates (see Section 5.8.3, “Call
Gates”). They contain a far pointer (segment selector and offset) that the processor
uses to transfer program execution to a handler procedure in an exception- or inter-
rupt-handler code segment. These gates differ in the way the processor handles the
IF flag in the EFLAGS register (see
Section 6.12.1.2, “Flag Usage By Exception- or
Interrupt-Handler Procedure”).
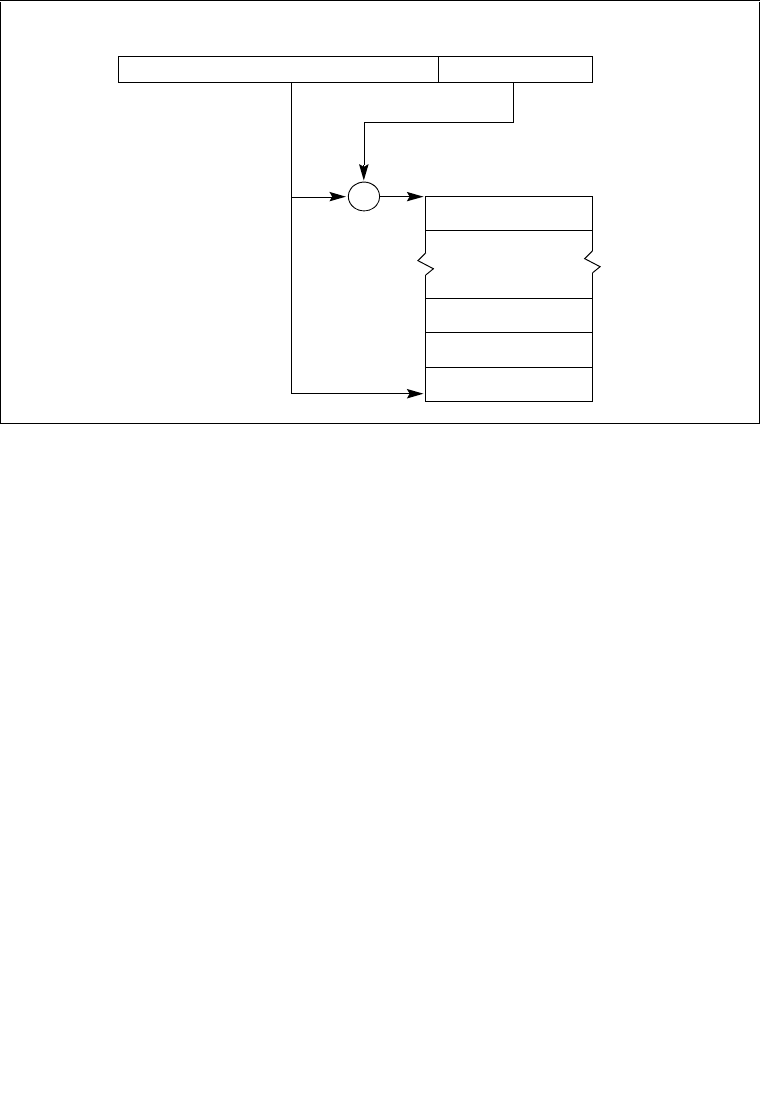
Figure 6-1. Relationship of the IDTR and IDT
IDT Limit
IDT Base Address
+
Interrupt
Descriptor Table (IDT)
Gate for
0
IDTR Register
Interrupt #n
Gate for
Interrupt #3
Gate for
Interrupt #2
Gate for
Interrupt #1
151647
0
31
0
8
16
(n−1)∗8


















