Vol. 3 11-23
MEMORY CACHE CONTROL
11.5.2.3 Writing Values Across Pages with Different Memory Types
If two adjoining pages in memory have different memory types, and a word or longer
operand is written to a memory location that crosses the page boundary between
those two pages, the operand might be written to memory twice. This action does not
present a problem for writes to actual memory; however, if a device is mapped the
memory space assigned to the pages, the device might malfunction.
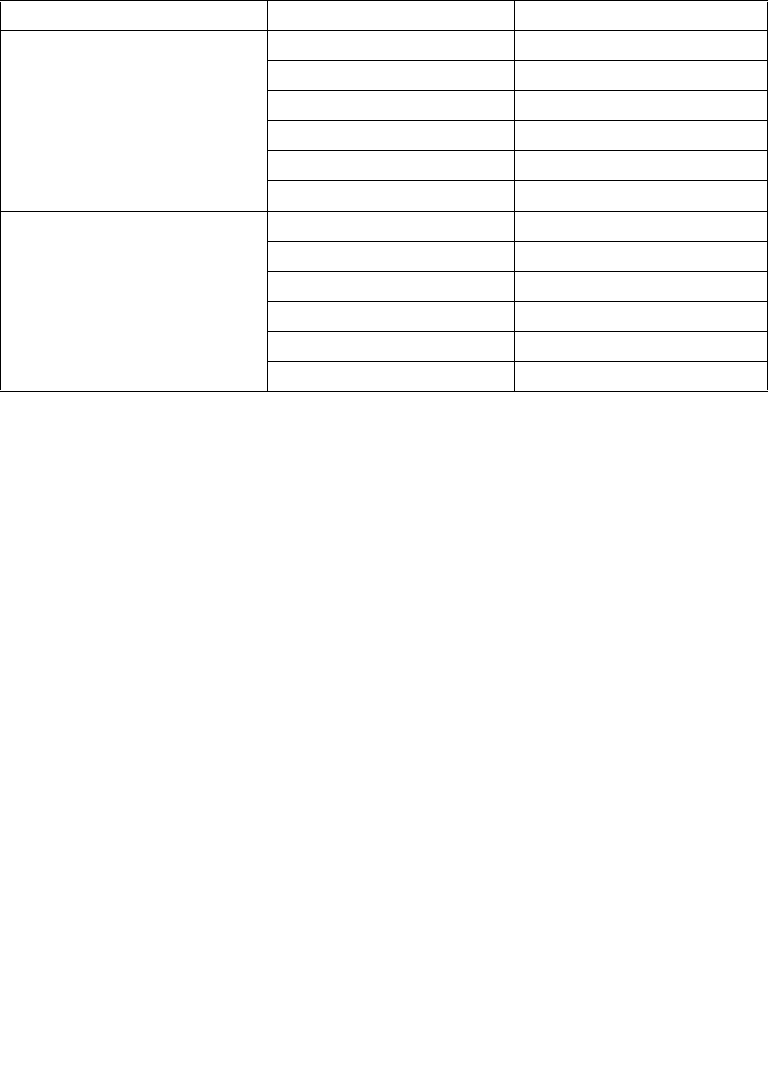
WB UC UC
2
UC- UC
2
WC WC
WT WT
WB WB
WP WP
WP UC UC
2
UC- WC
3
WC WC
WT WT
3
WB WP
WP WP
NOTES:
1. The UC attribute comes from the MTRRs and the processors are not required to snoop their
caches since the data could never have been cached. This attribute is preferred for performance
reasons.
2. The UC attribute came from the page-table or page-directory entry and processors are required
to check their caches because the data may be cached due to page aliasing, which is not recom-
mended.
3. These combinations were specified as “undefined” in previous editions of the Intel® 64 and IA-32
Architectures Software Developer’s Manual. However, all processors that support both the PAT
and the MTRRs determine the effective page-level memory types for these combinations as
given.
Table 11-7. Effective Page-Level Memory Types for Pentium III and More Recent
Processor Families (Contd.)
MTRR Memory Type PAT Entry Value Effective Memory Type


















