17-26 Vol. 3
8086 EMULATION
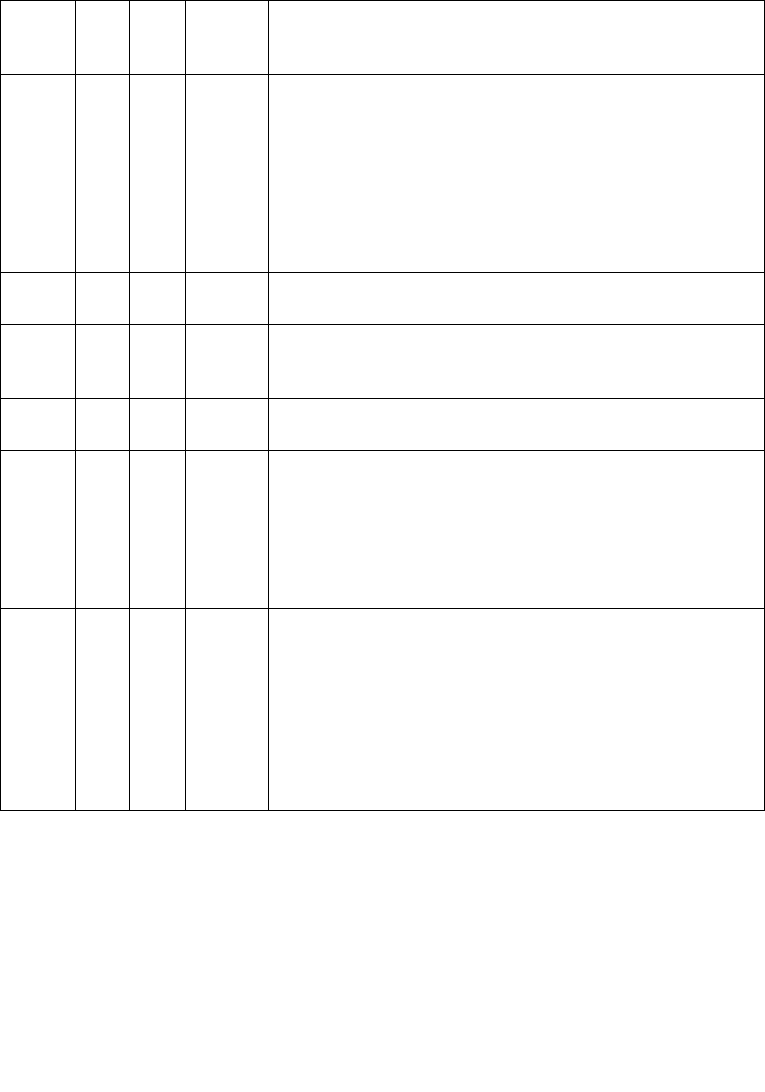
Table 17-2. Software Interrupt Handling Methods While in Virtual-8086 Mode
Method VME IOPL
Bit in
Redir.
Bitmap*
Processor Action
1 0 3 X Interrupt directed to a protected-mode interrupt handler:
• Switches to privilege-level 0 stack
• Pushes GS, FS, DS and ES onto privilege-level 0 stack
• Pushes SS, ESP, EFLAGS, CS and EIP of interrupted task onto
privilege-level 0 stack
• Clears VM, RF, NT, and TF flags
• If serviced through interrupt gate, clears IF flag
• Clears GS, FS, DS and ES to 0
• Sets CS and EIP from interrupt gate
2 0 < 3 X Interrupt directed to protected-mode general-protection
exception (#GP) handler.
3 1 < 3 1 Interrupt directed to a protected-mode general-protection
exception (#GP) handler; VIF and VIP flag support for handling
class 2 maskable hardware interrupts.
4 1 3 1 Interrupt directed to protected-mode interrupt handler: (see
method 1 processor action).
5 1 3 0 Interrupt redirected to 8086 program interrupt handler:
• Pushes EFLAGS
• Pushes CS and EIP (lower 16 bits only)
• Clears IF flag
• Clears TF flag
• Loads CS and EIP (lower 16 bits only) from selected entry in
the interrupt vector table of the current virtual-8086 task
6 1 < 3 0 Interrupt redirected to 8086 program interrupt handler; VIF and
VIP flag support for handling class 2 maskable hardware
interrupts:
• Pushes EFLAGS with IOPL set to 3 and VIF copied to IF
• Pushes CS and EIP (lower 16 bits only)
• Clears the VIF flag
• Clears TF flag
• Loads CS and EIP (lower 16 bits only) from selected entry in
the interrupt vector table of the current virtual-8086 task
NOTE:
* When set to 0, software interrupt is redirected back to the 8086 program interrupt handler;
when set to 1, interrupt is directed to protected-mode handler.


















