Vol. 3 5-43
PROTECTION
5.13 PAGE-LEVEL PROTECTION AND EXECUTE-DISABLE
BIT
In addition to page-level protection offered by the U/S and R/W flags, paging struc-
tures used with PAE paging and IA-32e paging (see Chapter 4) provide the execute-
disable bit. This bit offers additional protection for data pages.
An Intel 64 or IA-32 processor with the execute-disable bit capability can prevent
data pages from being used by malicious software to execute code. This capability is
provided in:
• 32-bit protected mode with PAE enabled.
• IA-32e mode.
While the execute-disable bit capability does not introduce new instructions, it does
require operating systems to use a PAE-enabled environment and establish a page-
granular protection policy for memory pages.
If the execute-disable bit of a memory page is set, that page can be used only as
data. An attempt to execute code from a memory page with the execute-disable bit
set causes a page-fault exception.
The execute-disable capability is supported only with PAE paging and IA-32e paging.
It is not supported with 32-bit paging. Existing page-level protection mechanisms
(see
Section 5.11, “Page-Level Protection”) continue to apply to memory pages inde-
pendent of the execute-disable setting.
5.13.1 Detecting and Enabling the Execute-Disable Capability
Software can detect the presence of the execute-disable capability using the CPUID
instruction. CPUID.80000001H:EDX.NX
[bit 20] = 1 indicates the capability is avail-
able.
If the capability is available, software can enable it by setting IA32_EFER.NXE[bit 11]
to 1. IA32_EFER is available if CPUID.80000001H.EDX[bit 20 or 29] = 1.
If the execute-disable capability is not available, a write to set IA32_EFER.NXE
produces a #GP exception. See
Table 5-4.
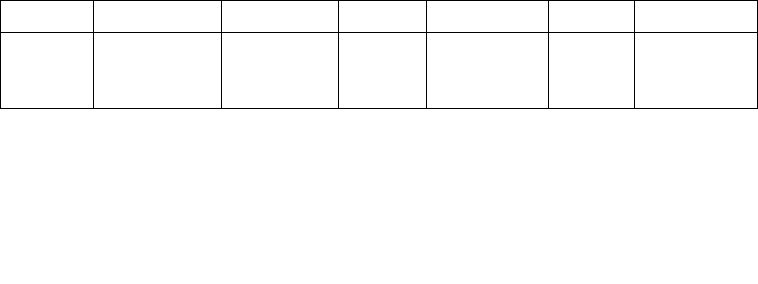
Table 5-4. Extended Feature Enable MSR (IA32_EFER)
63:12 11 10 9 8 7:1 0
Reserved Execute-
disable bit
enable (NXE)
IA-32e mode
active (LMA)
Reserve
d
IA-32e mode
enable (LME)
Reserve
d
SysCall enable
(SCE)


















