. . . . .
WORKING WITH THE CPU
MemoryManagement Unit (MMU)
www.digiembedded.com 111
First-level
descriptor bit
assignments:
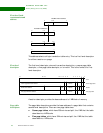
Priority encoding
of fault status
First-level
descriptor bit
assignments:
Interpreting first
level descriptor
bits [1:0]
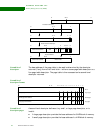
Section descriptor A section descriptor provides the base address of a 1 MB block of memory.
Section descriptor
format
Bits
Section Coarse Fine Description
[31:20] [31:10] [31:12] Forms the corresponding bits of the physical address.
[19:12] ---- ---
SHOULD BE ZERO
[11:10] --- --- Access permission bits. See “Access permissions and
domains” on page 106 and “Fault Address and Fault Status
registers” on page 119 for information about interpreting
the access permission bits.
9 9 [11:9]
SHOULD BE ZERO
[8:5] [8:5] [8:5] Domain control bits
444Must be 1.
[3:2] --- --- Bits C and B indicate whether the area of memory mapped
by this page is treated as write-back cachable, write-
through cachable, noncached buffered, or noncached
nonbuffered.
--- [3:2] [3:2]
SHOULD BE ZERO
[1:0] [1:0] [1:0] These bits indicate the page size and validity, and are
interpreted as shown in “First-level descriptor bit
assignments: Priority encoding of fault status” on
page 111.
Value Meaning Description
0 0 Invalid Generates a section translation fault.
0 1 Coarse page table Indicates that this is a coarse page table descriptor.
1 0 Section Indicates that this is a section descriptor.
1 1 Fine page table Indicates that this is a fine page table descriptor.
Section base address SBZ
S
B
Z
AP Domain 1 1 0CB
10234589101112192031