. . . . .
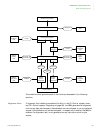
WORKING WITH THE CPU
Caches and write buffer
www.digiembedded.com 127
about the structure, replacement algorithm, or persistence of entries in the
set-associative part — specifically:
Any entry written into the set-associative part of the TLB can be removed at
any time. The set-associative part of the TLB must be considered as a
temporary cache of translation/page table information. No reliance must be
placed on an entry residing or not residing in the set-associative TLB unless
that entry already exists in the lockdown TLB. The set-associative part of the
TLB can contain entries that are defined in the page tables but do not
correspond to address values that have been accessed since the TLB was
invalidated.
The set-associative part of the TLB must be considered as a cache of the
underlying page table, where memory coherency must be maintained at all
times. To guarantee coherency if a level one descriptor is modified in main
memory, either an invalidate-TLB or Invalidate-TLB-by-entry operation must be
used to remove any cached copies of the level one descriptor. This is required
regardless of the type of level one descriptor (section, level two page
reference, or fault).
If any of the subpage permissions for a given page are different, each of the
subpages are treated separately. To invalidate all entries associated with a
page with subpage permissions, four MVA-based invalidate operations are
required — one for each subpage.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Caches and write buffer
The ARM926EJ-S processor includes an instruction cache (ICache), data cache
(DCache), and write buffer. The instruction cache is 8 KB in length, and the data
cache is 4 KB in length.
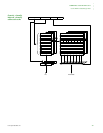
Cache features
The caches are virtual index, virtual tag, addressed using the modified virtual
address (MVA). This avoids cache cleaning and/or invalidating on context
switch.
The caches are four-way set associative, with a cache line length of eight
words per line (32 bytes per line), and with two dirty bits in the DCache.
The DCache supports write-through and write-back (copyback) cache
operations, selected by memory region using the C and B bits in the MMU
translation tables.
The caches support allocate on read-miss. The caches perform critical-word
first cache refilling.