I/O HUB MODULE
DMA controller
364 Hardware Reference NS9215 31 March 2008
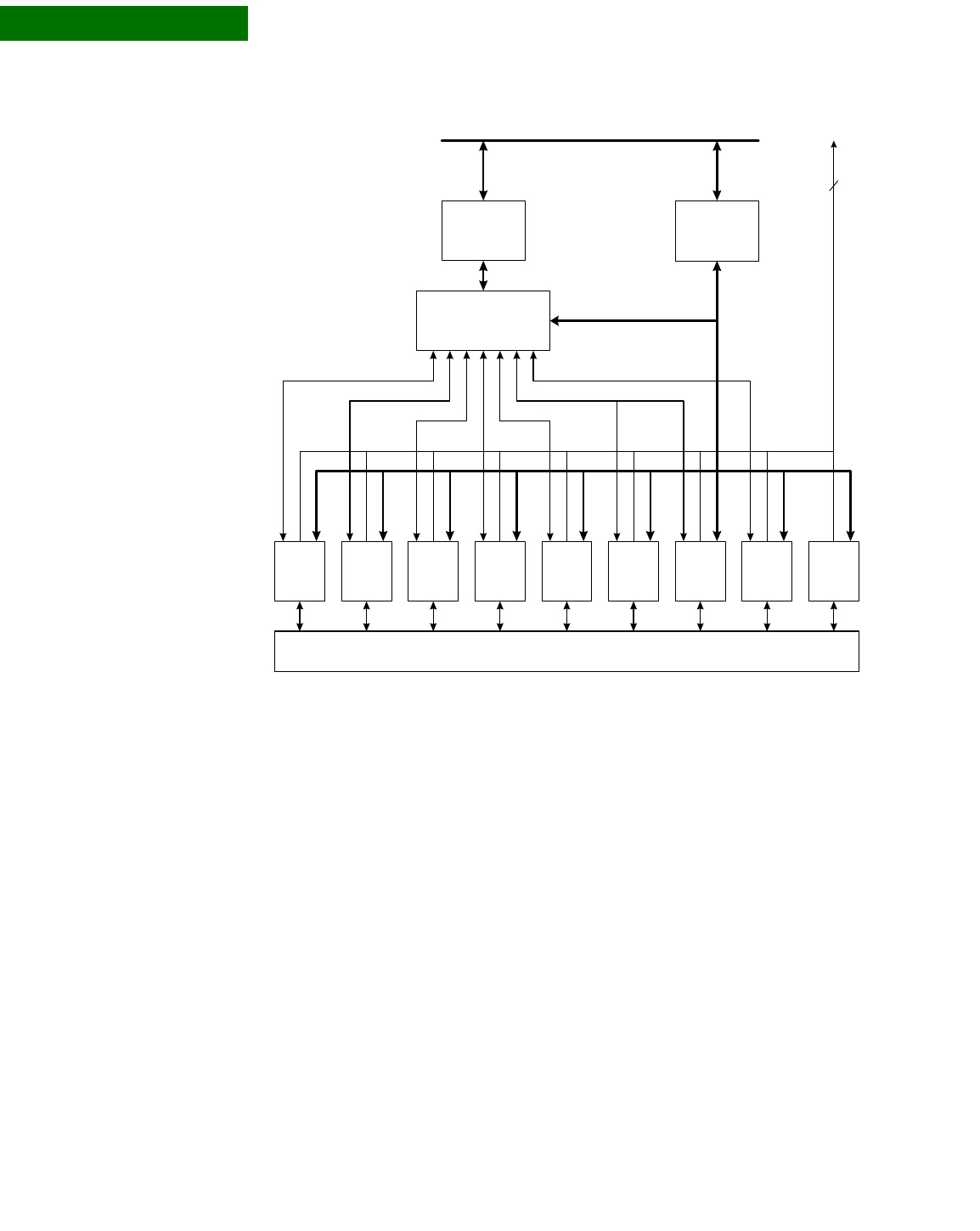
Block diagram
AHB slave
interface
The CPU has access to the control and status registers in the DMA controller, the
peripheral devices, and the GPIO configuration.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DMA controller
The processor provides an eight channel DMA controller to service the low speed
peripherals. Each channel has a transmit channel and a receive channel.
Servicing RX and
FIFOs
The DMA controller services the RX and FIFOs in a round-robin manner. When one of
the FIFOs needs servicing — that is, it can accept a burst of four 32-bit words — the
DMA controller requests the AHB bus through the AHB master. After the request has
been granted, the peripheral buffer data is transferred to or from system memory.
AMBA AHB Bus
AHB Master
DMA Controller
Rsvd UART ARsvd UART B UART C UART D A/D SPI I2C
AHB Slave
GPIO
to SCM Interrupt
Control ler