11. Robot Language Explanation
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
11 - 10
11.1.7 Operator
example
V10! = (V1!^2 + V2!^2 + V3!^2)*2.5
IF(V24!>=V50! AND V10$= “ WELD”
(1) Three operators are available in String
operation which are +(connection between two
strings), =(equal) and <>(difference).
(2) Pose operation can be used only in type of
<pose>+<shift>.
(3) ₩ is a integer division operator that the value
of left side's divided operator is divided by the value of right side's value and it
is rounded off.
(4) MOD is a operation that finds remainder of division.
(5) AND, OR, XOR are bit operators, and if you want to use it as a logical operator, we
recommend that operand should be 0 or 1. So at that time, the result can be accurate.
(6) NOT is only used as a bit operator, and logical NOT is not exist. So we recommend you
to use <> instead.
(7) In case of operation between integer and real number, integer is converted to real
number automatically and then the operation is executed.
(The result type of operation is real number type.)
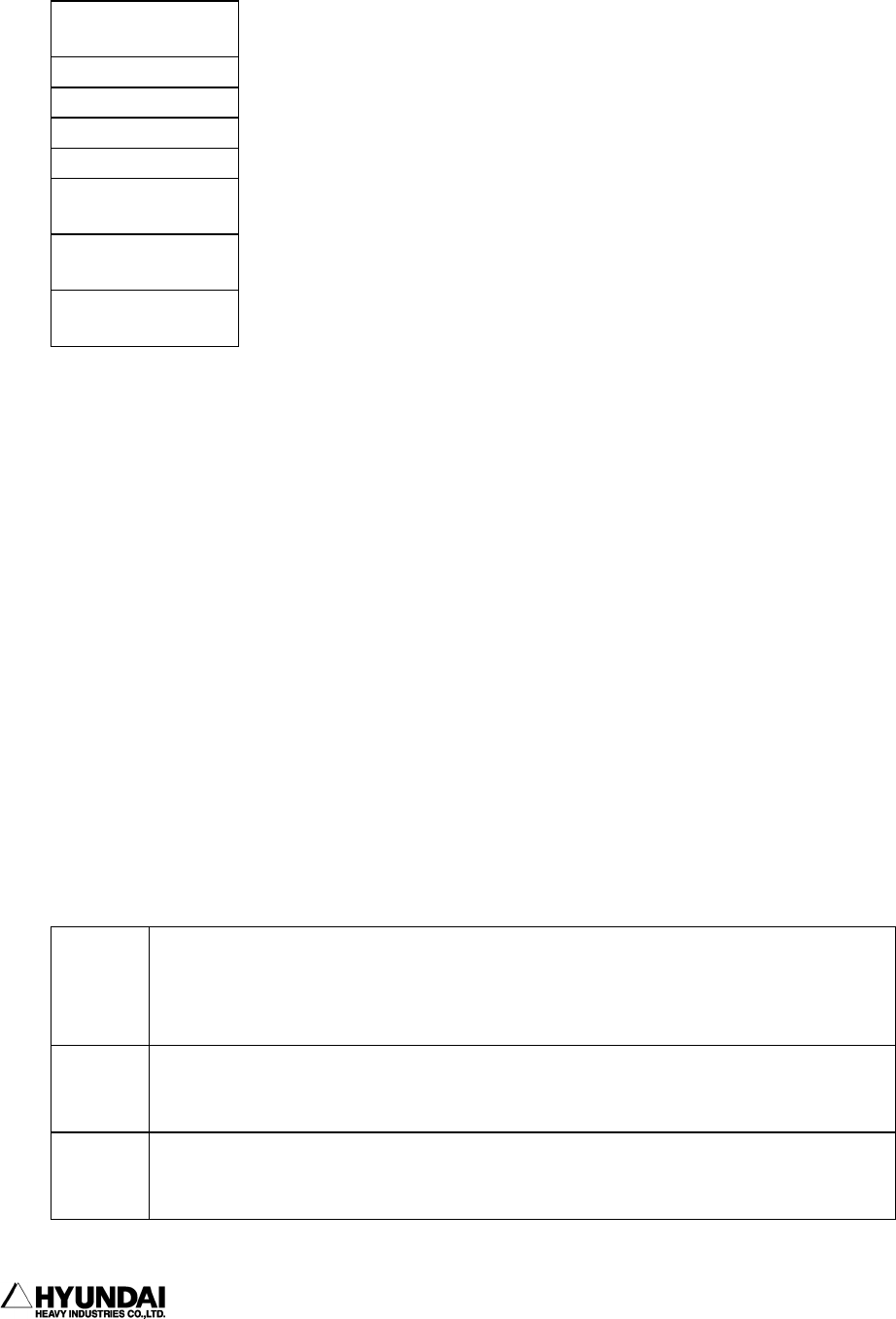
11.1.8 Formula
( )
high
p
riorit
sign(+ -) ↑
^
* / ₩ MOD
+ -
= <> < > <=
>=
NOT
↓
AND OR XOR
low
p
riorit
arithme-
tic
statement
Integer, real number, integer type variable, real number type variable,
arithmetic function, pose element, shift element, it includes operation which
has integer type or real number type in result.
Example: -10, 10.12, V1%, V1!, SQR(V1%), P1.X, R2.Y, (V2!+V3!)/2+&HC000
string
statement
String constant, string variable, string function, it includes operation which
has string type in result.
Example: "COMM ERR", "ABCD"+"EFCD", LEFT$("ROBOT INIT", 5)
pose
statement
Pose constant, pose variable, it includes operation which has pose type in result.
Example: (204.5, 37.35, 2.94, 0, 50, 0, 24)R+(0, 10, 0, 0, 0, 0)H, P1+R1


















