Hardware Reference Manual 137
Intel
®
IXP2800 Network Processor
Intel XScale
®
Core
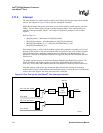
3.12.2 UART Overview
The UART performs serial-to-parallel conversion on data characters received from a peripheral
device and parallel-to-serial conversion on data characters received from the network processor.
The processor can read the complete status of the UART at any time during the functional
operation. Available status information includes the type and condition of the transfer operations
being performed by the UART and any error conditions (parity, overrun, framing, or break
interrupt).
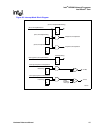
The serial ports can operate in either FIFO or non-FIFO mode. In FIFO mode, a 64-byte transmit
FIFO holds data from the processor to be transmitted on the serial link and a 64-byte receive FIFO
buffers data from the serial link until read by the processor.
The UART includes a programmable baud rate generator that is capable of dividing the clock input
by divisors of 1 to 2
16
- 1 and produces a 16X clock to drive the internal transmitter logic. It also
drives the receive logic. The UART has a processor interrupt system. The UART can be operated in
polled or in interrupt driven mode as selected by software.
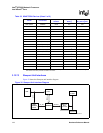
The UART has the following features
• Functionally compatible with National Semiconductor*’s PC16550D for basic receive and
transmit.
• Adds or deletes standard asynchronous communications bits (start, stop, and parity) to or from
the serial data
• Independently controlled transmit, receive, line status
• Programmable baud rate generator allows division of clock by 1 to (2
16
- 1) and generates an
internal 16X clock
• 5-, 6-, 7-, or 8-bit characters
• Even, odd, or no parity detection
• 1, 1½, or 2 stop bit generation
• Baud rate generation
• False start bit detection
• 64-byte Transmit FIFO
• 64-byte Receive FIFO
• Complete status reporting capability
• Internal diagnostic capabilities include:
— Break
— Parity
— Overrun
— Framing error simulation
• Fully prioritized interrupt system controls