380 Hardware Reference Manual
Intel
®
IXP2800 Network Processor
Performance Monitor Unit
11.1.6 Definition of Clock Domains
The following abbreviations are used in the events table under clock domain.
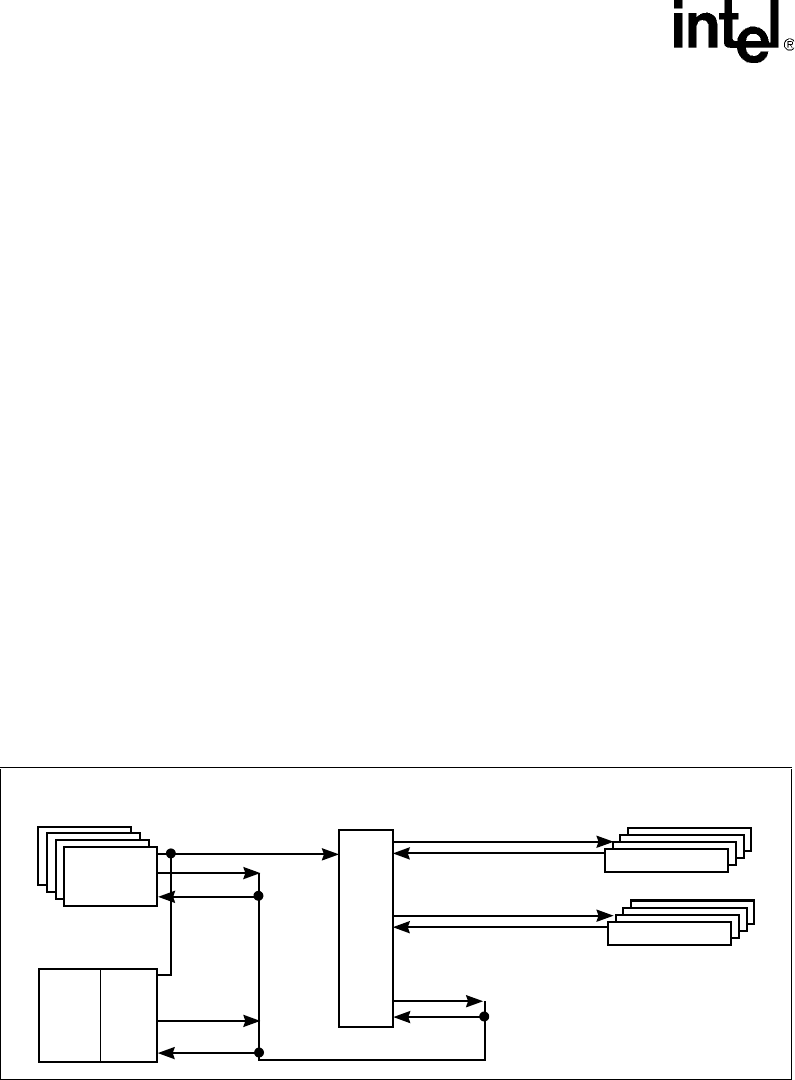
11.2 Interface and CSR Description
CAP is a standard logic block provided as part of the Network Processor that provides a method of
interfacing to the ARM APB. This bus supports standard APB peripherals such as PMU, UART,
Timers, and GPIO as well as CSRs that do not need to be accessed by the Microengines.
As shown in Figure 139, CAP uses three bus interfaces to support these modes. CAP supports a
target ID of 0101, which Microengine assemblers should identify as a CSR instruction.
Table 151 shows the Intel XScale
®
core and Microengine instructions used to access devices on
these buses and it shows which buses are used during the operation. For example, to read an APB
peripheral such as a UART CSR, a Microengine would execute a csr[read] instruction and the Intel
XScale
®
core would execute a Load (ld) instruction. Data is then moved between the CSR and the
Intel XScale
®
core/Microengine by first reading the CSR via the APB and then writing the result to
the Intel XScale
®
core/Microengine via the Push Bus.
P_CLK
The Command Push/Pull Clock also known as the Chassis clock. This clock is
derived from the Microengine (ME) Clock. It is one-half of the Microengine clock.
T_CLK Microengine Clock.
MTS_CLK MSF Flow Control Status LVTTL Clock TS_CLK.
MRX_CLK MSF Flow Control Receive LVDS Clock RX_CLK.
MR_CLK MSF Receive Data Clock R_CLK.
MT_CLK MSF Transmit Data Clock T_CLK.
MTX_CLK MSF Flow Control Transmit LVDS Clock TX_CLK.
D_CLK DRAM Clock.
S_CLK SRAM Clock.
APB_CLK Advance Peripheral Bus Clock.
Figure 139. CAP Interface to the APB
Bus Masters
(e.g. ME)
Gasket
Intel
XScale
®
Core
APB Peripheral
CSRs (std or fast)
CAP
APB Bus
CSR Command
CAP CSR Bus
Source/Target Interfaces
Push/Pull Bus


















