222 Hardware Reference Manual
Intel
®
IXP2800 Network Processor
SRAM Interface
The external coprocessor interface is based on FIFO communication.
A thread can send parameters to the coprocessor by doing a normal SRAM write instruction:
sram[write, $sram_xfer_reg, src1, src2, ref_count], optional_token
The number of parameters (longwords) passed is specified by ref_count. The address can be
used to support multiple coprocessor FIFO ports. The coprocessor performs some operation using
the parameters, and then will later pass back some number of results values (the number of
parameters and results will be known by the coprocessor designers). The time between the input
parameter and return values is not fixed; it is determined by the amount of time the coprocessor
requires to do its processing and can be variable. When the coprocessor is ready to return the
results, it signals back to the SRAM controller through a mailbox-valid bit that the data in the read
FIFO is valid. A thread can get the return values by doing a normal SRAM read instruction:
sram[read, $sram_xfer_reg, src1, src2, ref_count], optional_token
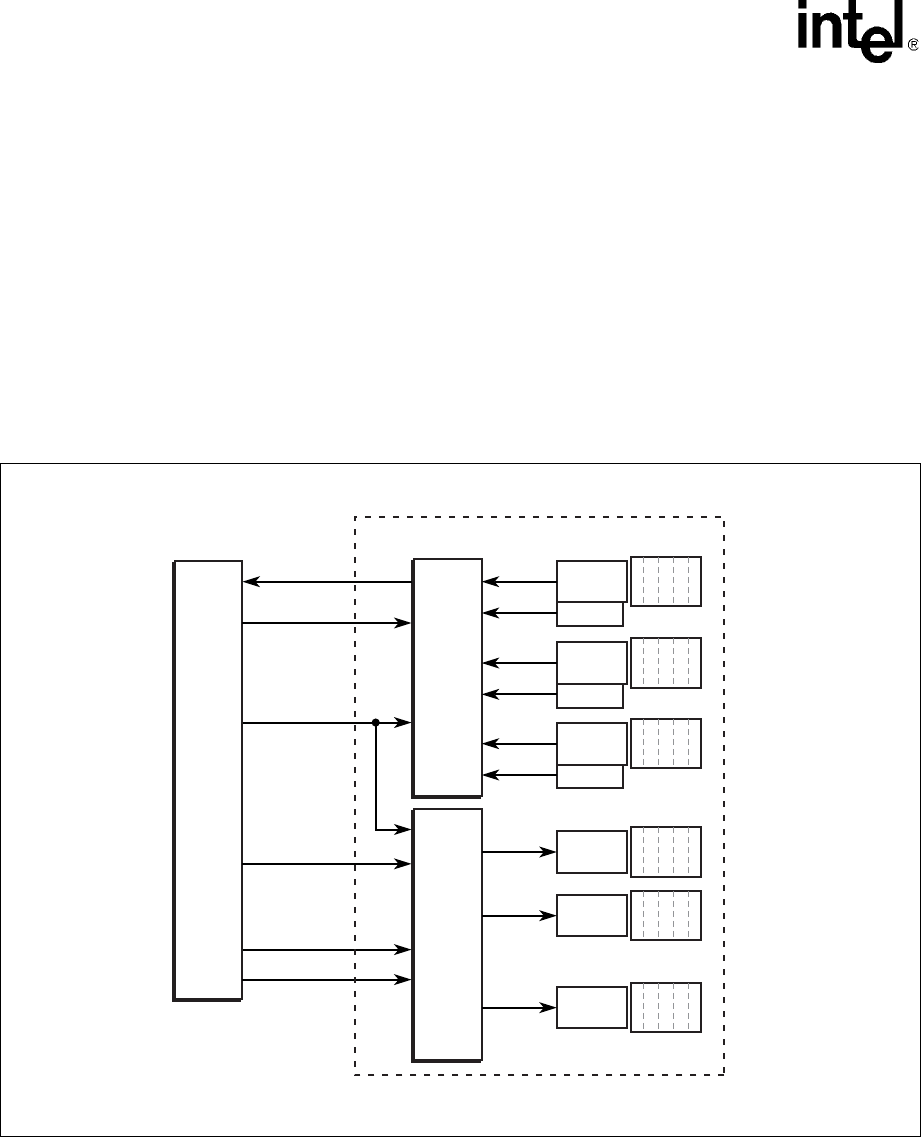
Figure 83 shows the coprocessor with 1-to-n memory-mapped FIFO ports.
If the read instruction executes before the return values are ready, the coprocessor signals
data-invalid through the mailbox register on the read data bus (
Qn[17:0]). Signaling a thread
upon pushing its read data works exactly as in a normal SRAM read.
Figure 83. Coprocessor with Memory Mapped FIFO Ports
A9749-01
Read
Control
Logic
Port 1
Mail Box
FIFO
Valid
Write
Control
Logic
Port 2
Mail Box
Valid
Port n
Mail Box
Valid
Network Processor
Coprocessor
Qn[17:0]
RPE_Ln[0]
BWEn[1:0]
WPE_Ln[0]
Dn[17:0]
An[x:0]
……
Port 1
Mail Box
FIFO
Port 2
Mail Box
FIFO
Port n
Mail Box
FIFO
FIFO
FIFO