Hardware Reference Manual 219
Intel
®
IXP2800 Network Processor
SRAM Interface
6.7 Reference Ordering
This section describes the ordering between accesses to any one SRAM controller. Various
mechanisms are used to guarantee order — for example, references that always go to the same
FIFOs remain in order. There is a CAM associated with write addresses that is used to order reads
behind writes. Lastly, several counter pairs are used to implement “fences”. The input counter is
tagged to a command and the command is not permitted to execute until the output counter
matches the fence tag. All of this will be discussed in more detail in this section.
6.7.1 Reference Order Tables
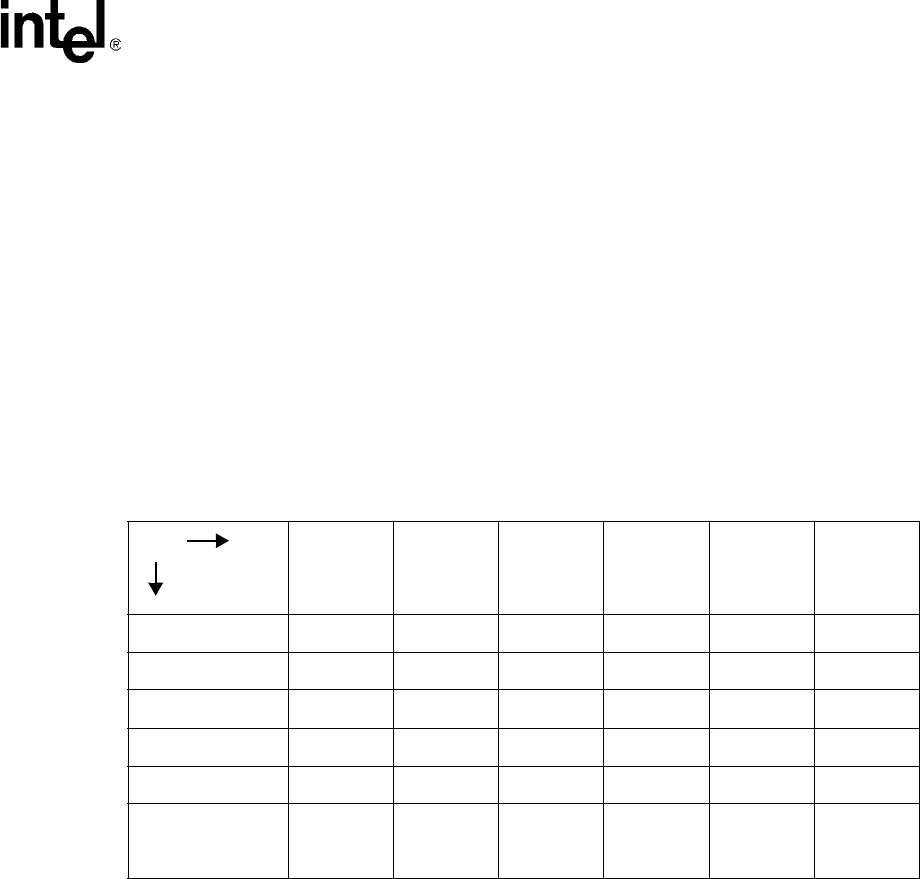
Table 77 shows the architectural guarantees of order of accesses to the same SRAM address
between a reference of any given type (shown in the column labels) and a subsequent reference of
any given type (shown in the row labels). The definition of first and second is defined by the time
the command is valid on the command bus. Verification requires testing only the order rules shown
in Table 77 and Table 78. Note that a blank entry means no order is enforced.
Table 78 shows the architectural guarantees of order to access to the same
SRAM Q_array entry
between a reference of any given type (shown in the column labels) and a subsequent reference of
any given type (shown in the row labels). The terms first and second are defined with reference to
the time the command is valid on the command bus. The same caveats that apply to Table 77 apply
to Table 78.
Table 77. Address Reference Order
1
st
ref
2
nd
ref Memory
Read
CSR Read
Memory
Write
CSR Write Atomics
Queue /
Ring /
Q_Descr
Commands
Memory Read Order Order
CSR Read Order
Memory Write Order Order
CSR Write Order
Atomics Order Order
Queue / Ring /
Q_ Descr
Commands
See
Table 78.