697 | VoiceandVideo DellPowerConnectW-SeriesArubaOS6.2 | User Guide
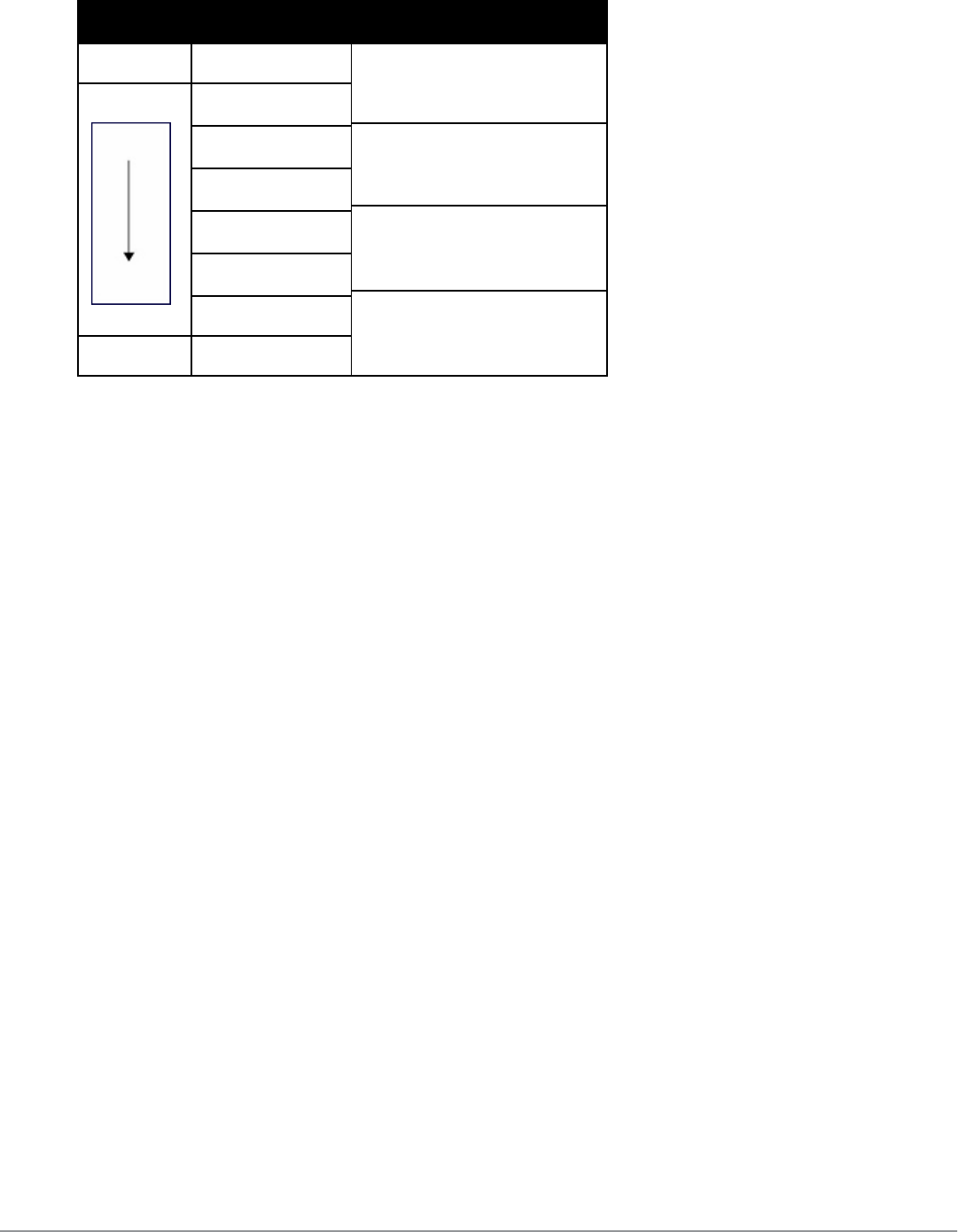
Priority 802.1p Priority WMM Access Category
Lowest 1 Background
2
0 Best effort
3
4 Video
5
6 Voice
Highest 7
Table 300:
WMM Access Category to 802.1p Priority Mapping
In non-WMM, or hybrid environments where some clients are not WMM-capable, Dell uses voice and best effort to
prioritize traffic from these clients.
Unscheduled Automatic Power Save Delivery (U-APSD) is a component of the IEEE 802.11e standard that extends
the battery life on voice over WLAN devices. When enabled, clients trigger the delivery of buffered data from the AP
by sending a data frame.
For the environments in which the wireless clients support WMM, you can enable both WMM and U-APSD in the
SSID profile.
Enabling WMM
You can use the WebUI or CLI to enable WMM for wireless clients.
In the WebUI
1. Navigate to the Configuration > Wireless > AP Configuration page.
2. Select either the AP Group or AP Specific tab. Click Edit for the AP group or AP name.
3. In the Profiles list, select Wireless LAN. Select Virtual AP, then select the applicable virtual AP profile. Select
the SSID profile.
4. In the Profile Details, select the Advanced tab.
5. Select the Wireless Multimedia (WMM) option. Or, select the Wireless Multimedia U-APSD (WMM-UAPSD)
Powersave option if you want to enable WMM in power save mode.
6. Click Apply.
In the CLI
wlan ssid-profile <profile> wmm
wlan ssid-profile <profile> wmm-uapsd
Configuring WMM AC Mapping
The IEEE 802.11e standard defines the mapping between WMM ACs and Differentiated Services Codepoint
(DSCP) tags. The WMM AC mapping commands allow you to customize the mapping between WMM ACs and
DSCP tags to prioritize various traffic types. You apply and configure WMM AC mappings to a WMM-enabled
SSID profile.


















