732 | W-600Series Controllers DellPowerConnectW-SeriesArubaOS6.2 | User Guide
Connecting with a USB Cellular Modems
USB Cellular Modems are supported via a USB port. ArubaOS supports several EVDO (Evolution Data Optimized,
up to 3.1 Mbps, CDMA) and 3G HSPA (High-Speed Packet Access, 3G data service) modems. The 3G HSPA is
provided by AT&T in the United States and numerous other 3G providers worldwide.
How it Works
Plug the USB Cellular Modem into the USB port of the W-600 Series controller. The USB Cellular Modem is
automatically detected and negotiates a PPP IP address. If the modem fails to obtain a PPP IP address within 45
seconds, the controller ignores the modem’s presence, and boots as if the modem is not present.
Switching Modes
Many of the newer modems contain multiple USB devices; creating a very elegant plug-n-play solution. When your
USB Cellular Modem is first powered on, a storage device is registered. This storage device contains the software
driver/executable necessary to install and operate the modem.
Once the software installation is complete, the modem must
mode-switch
from a storage device to a registered
modem device. Mode-switching varies by manufacturer. For example, The Novatel modem mode-switches via a SCSI
eject command; the Huawei modem mode-switches via a SCSI rezero command, while the Sierra modem mode-
switches via a specific USB command. Once the mode-switching is complete, the modem automatically registers
itself.
The controller can dial (via the modem) your Service Provider to initiate a PPP session. During the boot sequence,
the controller issues your device’s mode-switching command, every few seconds, until the PPP link connects.
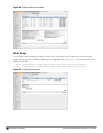
Finding USB Modem Commands
To support the USB cellular modems on the W-600 Series cellular specific commands are available at the command
line (see Figure 322 and Figure 323). For detailed information on these commands, refer to the Command Line
Reference Guide.
Figure 322: Cellular Profile Commands
Figure 323 list the Uplink commands.
Figure 323: Uplink Commands