User’s Manual
PPC440x5 CPU Core Preliminary
Page 172 of 589
intrupts.fm.
September 12, 2002
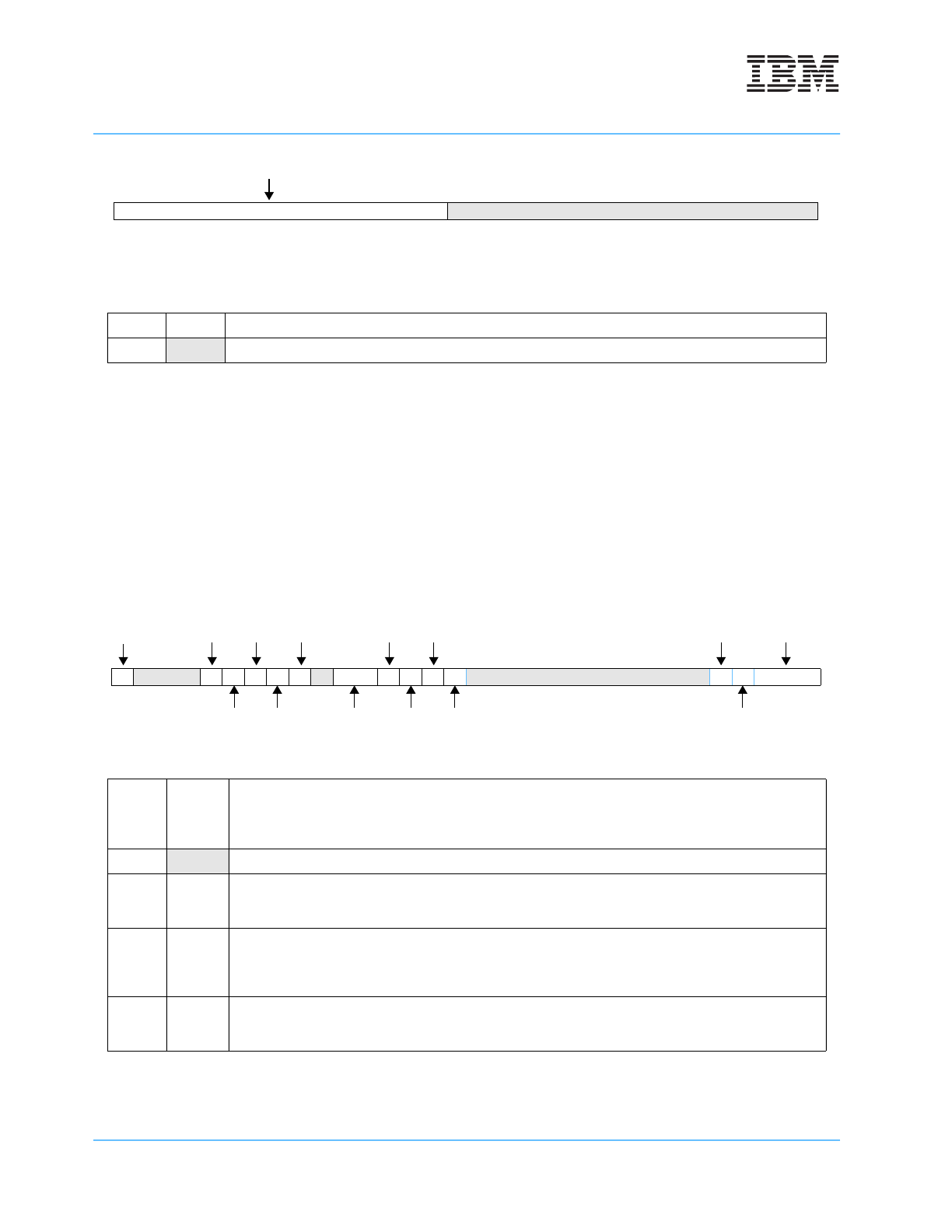
6.4.11 Exception Syndrome Register (ESR)
The ESR provides a syndrome to differentiate between the different kinds of exceptions that can generate the
same interrupt type. Upon the generation of one of these types of interrupt, the bit or bits corresponding to the
specific exception that generated the interrupt is set, and all other ESR bits are cleared. Other interrupt types
do not affect the contents of the ESR. Figure 6-10 on page 172 provides a summary of the fields of the ESR
along with their definitions. See the individual interrupt descriptions under Interrupt Definitions on page 175
for an explanation of the ESR settings for each interrupt type, as well as a more detailed explanation of the
function of certain ESR fields.
The ESR can be written from a GPR using mtspr, and can be read into a GPR using mfspr.
Figure 6-9. Interrupt Vector Prefix Register (IVPR)
0:15 IVP Interrupt Vector Prefix
16:31 Reserved
Figure 6-10. Exception Syndrome Register (ESR)
0 MCI
Machine Check—Instruction Fetch Exception
0 Instruction Machine Check exception did not
occur.
1 Instruction Machine Check exception occurred.
This is an implementation-dependent field of the
ESR and is not part of the PowerPC Book-E Archi-
tecture.
1:3 Reserved
4 PIL
Program Interrupt—Illegal Instruction Exception
0 Illegal Instruction exception did not occur.
1 Illegal Instruction exception occurred.
5 PPR
Program Interrupt—Privileged Instruction Excep-
tion
0 Privileged Instruction exception did not occur.
1 Privileged Instruction exception occurred.
6 PTR
Program Interrupt—Trap Exception
0 Trap exception did not occur.
1 Trap exception occurred.
01516 31
IVP
0 1 3456789 10111213141516 26 27 28 29 31
MCI PIL
PPR
PTR
FP
DLK
AP
PUO
BO
ST
PIE
PCRE PCRF
PCMP


















