User’s Manual
Preliminary PPC440x5 CPU Core
prgmodel.fm.
September 12, 2002
Page 47 of 589
2.2 Registers
This section provides an overview of the register categories and types provided by the PPC440x5. Detailed
descriptions of each of the registers are provided within the chapters covering the functions with which they
are associated (for example, the cache control and cache debug registers are described in Instruction and
Data Caches on page 95). An alphabetical summary of all registers, including bit definitions, is provided in
Register Summary on page 451
All registers in the PPC440x5 core are architected as 32 bits wide, although certain bits in some registers are
reserved and thus not necessarily implemented. For all registers with fields marked as reserved, these
reserved fields should be written as 0 and read as undefined. The recommended coding practice is to
perform the initial write to a register with reserved fields set to 0, and to perform all subsequent writes to the
register using a read-modify-write strategy: read the register; use logical instructions to alter defined fields,
leaving reserved fields unmodified; and write the register.
All of the registers are grouped into categories according to the processor functions with which they are asso-
ciated. In addition, each register is classified as being of a particular type, as characterized by the specific
instructions which are used to read and write registers of that type. Finally, most of the registers contained
within the PPC440x5 core are defined by the Book-E Enhanced PowerPC Architecture, although some regis-
ters are implementation-specific and unique to the PPC440x5.
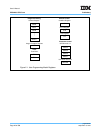
Figure 2-1 on page 48 illustrates the PPC440x5 registers contained in the user programming model, that is,
those registers to which access is non-privileged and which are available to both user and supervisor
programs. Figure 2-2 on page 49 illustrates the PPC440x5 registers contained in the supervisor program-
ming model, to which access is privileged and which are available to supervisor programs only. See User and
Supervisor Modes on page 80 for more information on privileged instructions and register access, and the
user and supervisor programming models.
Table 2-3 on page 50, lists each register category and the registers that belong to each category, along with
their types and a cross-reference to the section of this document which describes them more fully. Registers
that are not part of PowerPC Book-E, and are thus specific to the PPC440x5, are shown in italics in
Table 2-3. Unless otherwise indicated, all registers have read/write access.