CHAPTER 6 IMAGE FORMATION SYSTEM
6-16
COPYRIGHT
©
2000 CANON INC. CANON imageRUNNER 600 REV.1 JAN. 2000 PRINTED IN U.S.A.
III . CONTROLLING THE CHARGING MECHANISMS
A. Controlling the Primary Charging Mechanism
1. Outline
Part 2>Chapter 5>4.2
The primary charging mechanism is controlled for the following:
[1] Primary charging bias constant current
[2] Grid bias constant voltage
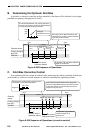
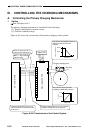
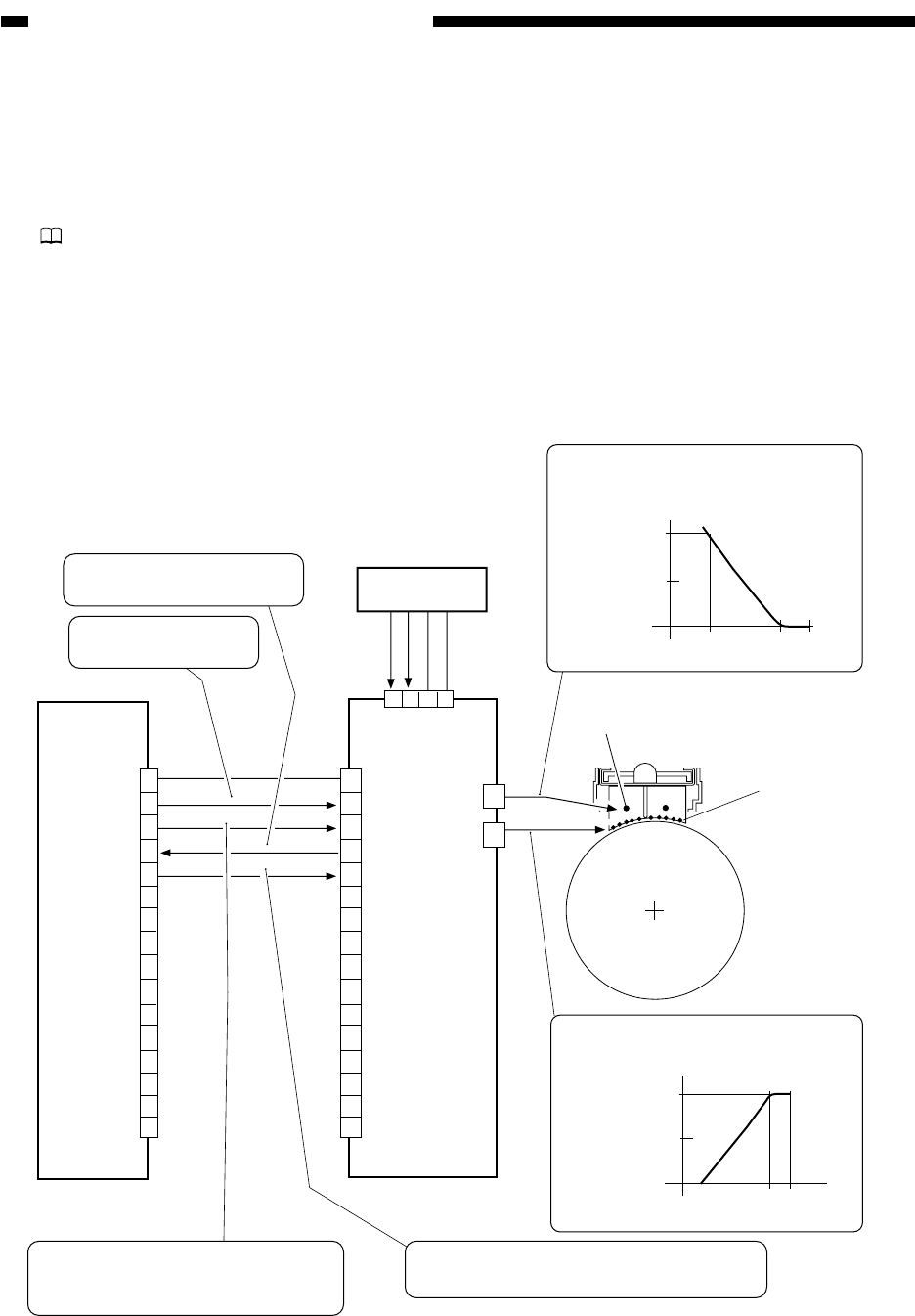
Figure 6-301 shows the construction of the primary charging control system.
Figure 6-301 Construction of the Control System
DC controller PCB
High-voltage DC PCB
J510A J723
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
0 V
24 VH
24 VH
HVDC-EN
PR-CNT
GRD-CNT
PR-ERR
GND
GND
1
2
3
4
Relay PCB
Primary charging wire
Grid wire
T601
J731
3V
11V
12V
1600µA
800µA
900V
400V
PR-CNT
3V
11V
GRD-CNT
12V
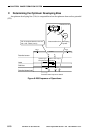
Grid bias
Primary charging bias
The primary charging bias varies as
follows according to PR-CNT
potential.
The grid bias varies as follows
according to GRD-CNT potential.
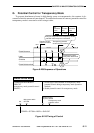
When an overcurrent or an
undercurrent is detected, '0'.
When '1', high-voltage
output is ready.
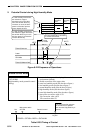
A voltage input between 0 and 12 V,
used to control the current level of the
primary bias.
A voltage input between 0 and 12 V, used to
control the voltage level of the grid bias.