TMP92CZ26A
92CZ26A-243
3.11.3.1 Differences between Hamming Codes and Reed-Solomon Codes
The NDFC includes an ECC generator supporting NAND Flash memory devices of SLC
(or 2LC: two states) type and MLC (or 4LC: four states) type.
The ECC calculation using Hamming codes (supporting SLC) generates 22 bits of ECC
for every 256 bytes of valid data and is capable of detecting and correcting a single-bit error
for every 256 bytes. Error bit detection calculation and correction must be implemented by
software. When using SmartMedia™, Hamming codes should be used.
The ECC calculation using Reed-Solomon codes (supporting MLC) generates 80 bits of
ECC for every 1 byte to 518 bytes of valid data and is capable of detecting and correcting
error bits at four addresses for every 518 bytes. When using Reed-Solomon codes, error bit
detection calculation is supported by hardware and only error bit correction needs to be
implemented by software.
The differences between Hamming codes and Reed-Solomon codes are summarized in
Table 3.11.1.
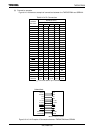
Table 3.11.1 Differences between Hamming Codes and Reed-Solomon Codes
Hamming Reed-Solomon
Maximum number of
correctable errors
1 bit 4 addresses
(All the 8 bits at one address are correctable.)
Number of ECC bits 22 bits/256 bytes 80 bits/up to 518 bytes
Error bit detection
method
Software Hardware
Error bit correction
method
Software Software
Error bit detection time Depends on the software to be used. See the table below.
Others Supports SmartMedia™. -
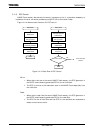
Number of
Error Bits
Reed-Solomon Error Bit
Detection Time (Unit: Clocks)
Notes
4 813 (max)
3 648 (max)
2 358 (max)
1 219 (max)
0 1
These values indicate the total number of clocks for
detecting error bit(s) not including the register read/write
time by the CPU.