TMP92CZ26A
92CZ26A-506
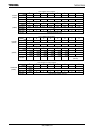
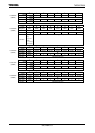
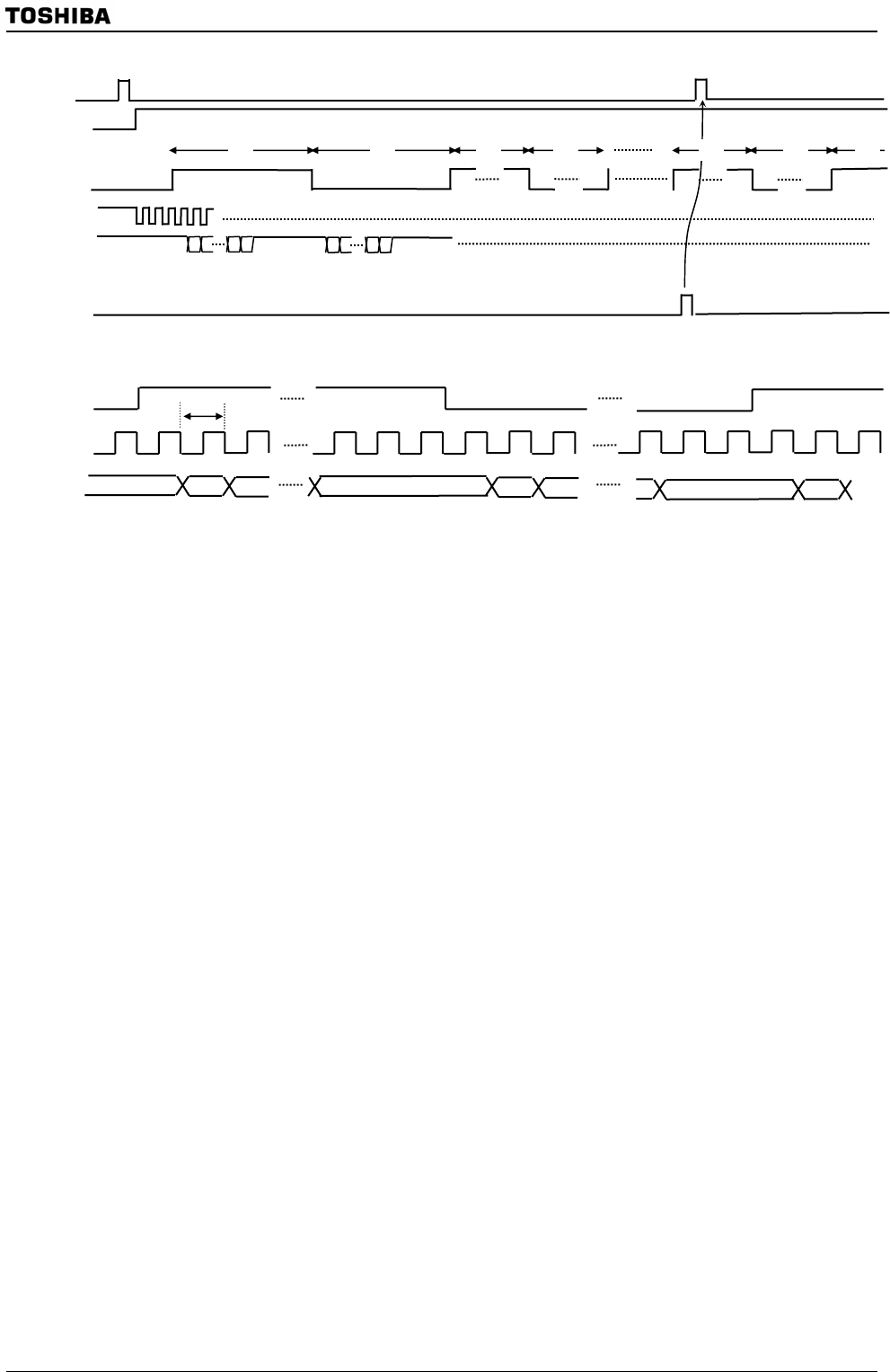
Figure 3.18.6 Timing Diagrams (I2S FMT/Stereo/16bit/MSB first)
(3) Considerations for using the I
2
S unit
1) INTI2Sn generation timing
Every 4bytes data trance from FIFO buffer to shift register per one time.
An INTI2Sn interrupt is generated under two conditions. One is when there are 64
bytes of empty space in the FIFO (after 61- 64th byte has been transferred to the shift
register). The other is when the FIFO becomes completely empty (after 125 - 128th
byte has been transferred to the shift register). Therefore, INTI2Sn indicates that
there are 64 bytes or 128 bytes of empty space in the FIFO, enabling the next data to
be written.
The FIFO must be written in units of 64 bytes. Since the FIFO can contain 128 bytes
of data, I
2
S output can be performed continuously as long as there are 64 bytes of data
in the FIFO. It is also possible to check the FIFO state by using the
I2SnCTL<TEMPn> flag.
2) I2SnCTL<TXEn>
Transmission is started by setting I2SnCTL <TXEn> to “1”. Once <TXEn> is set to
“1”, transmission is continued automatically as long as the FIFO contains the data to
be transmitted. While <TXE> is set to “1” (transmission in progress), the other bits in
the I2SnCTL register must not be changed.
To stop transmission, make sure that the FIFO is empty by checking the
I2SnCTL<TEMPn> flag. Then, after waiting for two periods of the I2SWS signal (after
all the data has been transmitted), set <TXEn> to “0”. In case monaural setting, make
sure that the FIFO is empty by checking the I2SnCTL<TEMPn> flag. Then, after
waiting for four periods of the I2SWS signal (after all the data has been transmitted),
set <TXEn> to “0”.
If <TXEn> is set to “0” while data is being transmitted, the transmission is stopped
FIFO write
<TXE>
I2SnWS pin
I2SnCKO pin
I2SnDO pin
INTI2Sn
1 3 31 33
Overall Timing Diagram
LSB
MSB
LSB
MSB
LSB
MSB
I2SnWS pin
I2SnCKO pin
I2SnDO pin
Detailed Timing Diagram
400kHz
Bit15 Bit14 Bit0 Bit15 Bit14
Bit0
Bit15
2 4 32