Section 3 DSP Operation
Rev. 4.00 Sep. 14, 2005 Page 119 of 982
REJ09B0023-0400
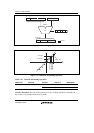
X pointer (R4, R5)
0, +2, +R8
XAB [15:1] YAB [15:1]
XDB [15:0] YDB [15:0]
0, +2, +R9
Y pointer (R6, R7)
X memory
(RAM, ROM)
Y memory
(RAM, ROM)
Not affected for store and cleared for load Cannot be specitied
X0
X1
Y0
Y1
M0
M1
A0G A1G DSR
A0
A1
Figure 3.14 Data Transfer Operation Flow
Type 2 instructions execute just two data transfer operations. The 16-bit instruction code is used
for this type of instructions. Basically, operation and operand flexibility are the same as in type 1
but conditional operation is not supported. This type of data transfer operation can access X or Y
memory only. Any other memory space cannot be accessed.
Type 3 instructions execute single data transfer operations only. The 16-bit instruction code is
used for this type of instructions. X pointers and other two extra pointers are available for this type
of operation, but Y pointers are not available. This type of operation can access any memory
address space, and all registers in the DSP unit, except for DSR, can be specified for both source
and destination operands. The guard-bit registers, A0G and A1G, can also be specified as
independent registers.
This type of operation can treat both single-word data and longword data. When a word-data
transfer operation is executed, the upper word of the register operand is activated. In case of word
data load, the data is loaded into the upper word of the destination register, the lower side of the
destination register is automatically cleared, and the signed bit is copied into the guard-bit parts, if
supported. In case of longword data load, the data is loaded into the upper word and lower word of
the destination register and the signed bit is sign-extended and copied into the guard-bit parts, if
supported. In case of the guard register store, the signed bit is sign-extended and copied on the
upper 24 bits of LDB. Figures 3.15 and 3.16 show this type of data transfer operation flows.