Section 19 Serial Communication Interface with FIFO (SCIF)
Rev. 4.00 Sep. 14, 2005 Page 734 of 982
REJ09B0023-0400
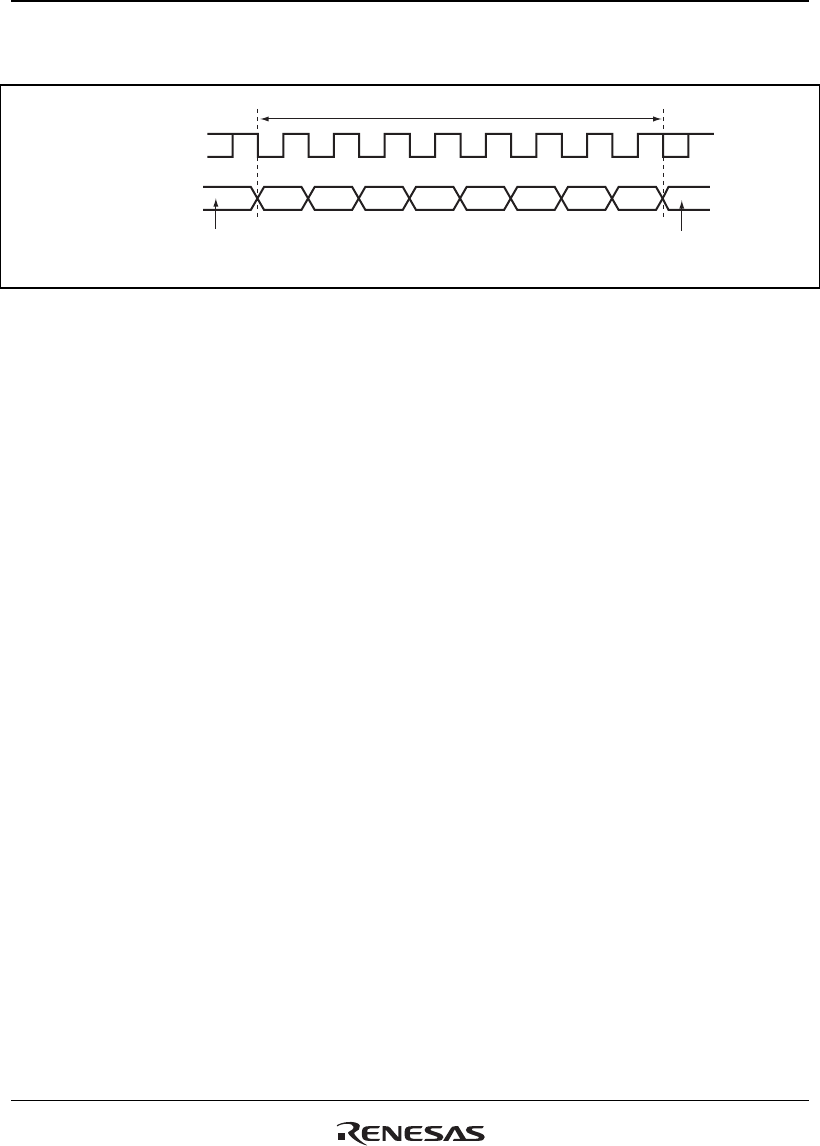
Figure 19.11 shows the general format in synchronous serial communication.
Don't
care
Don’t
care
One unit of transfer data (character or frame)
Bit 0
Serial data
Synchronization
clock
Bit 1 Bit 3 Bit 4 Bit 5
LSB
MSB
Bit 2 Bit 6 Bit 7
*
*
Note: * High except in continuous transfer
Figure 19.11 Data Format in Synchronous Communication
In synchronous serial communication, each data bit is output on the communication line from one
falling edge of the serial clock to the next. Data is guaranteed valid at the rising edge of the serial
clock. In each character, the serial data bits are transmitted in order from the LSB (first) to the
MSB (last). After output of the MSB, the communication line remains in the state of the MSB. In
synchronous mode, the SCIF transmits or receives data by synchronizing with the rising edge of
the serial clock.
Transmit/Receive Formats: The data length is fixed at eight bits. No parity bit can be added.
Clock: An internal clock generated by the on-chip baud rate generator or an external clock input
from the SCK pin can be selected as the SCIF transmit/receive clock.
When the SCIF operates on an internal clock, it outputs the clock signal at the SCK pin. Eight
clock pulses are output per transmitted or received character. When the SCIF is not transmitting or
receiving, the clock signal remains in the high state. When only receiving, the clock signal outputs
while the RE bit of SCSCR is 1 and the number of data in receive FIFO is less than the receive
FIFO data trigger number.
Transmitting and Receiving Data:
• SCIF Initialization (Synchronous Mode)
Before transmitting, receiving, or changing the mode or communication format, the software must
clear the TE and RE bits to 0 in the serial control register (SCSCR), then initialize the SCIF.
Clearing TE to 0 initializes the transmit shift register (SCTSR). Clearing RE to 0, however, does
not initialize the RDF, PER, FER, and ORER flags and receive data register (SCRDR), which
retain their previous contents.