Section 12 Bus State Controller (BSC)
Rev. 4.00 Sep. 14, 2005 Page 387 of 982
REJ09B0023-0400
The burst ROM interface performs burst operations for all read accesses. For example, in a
longword access over a 16-bit bus, valid 16-bit data is read two times and invalid 16-bit data is
read six times. These invalid data read cycles increase the memory access time and degrade the
program execution speed and DMA transfer speed. To prevent this problem, it is recommend
using a 16-byte read by cache fill or 16-byte read by the DMAC. Thus, the burst ROM (clock
synchronous) should be accessed with the cache having been set on. The burst ROM interface
performs write accesses in the same way as normal space access.
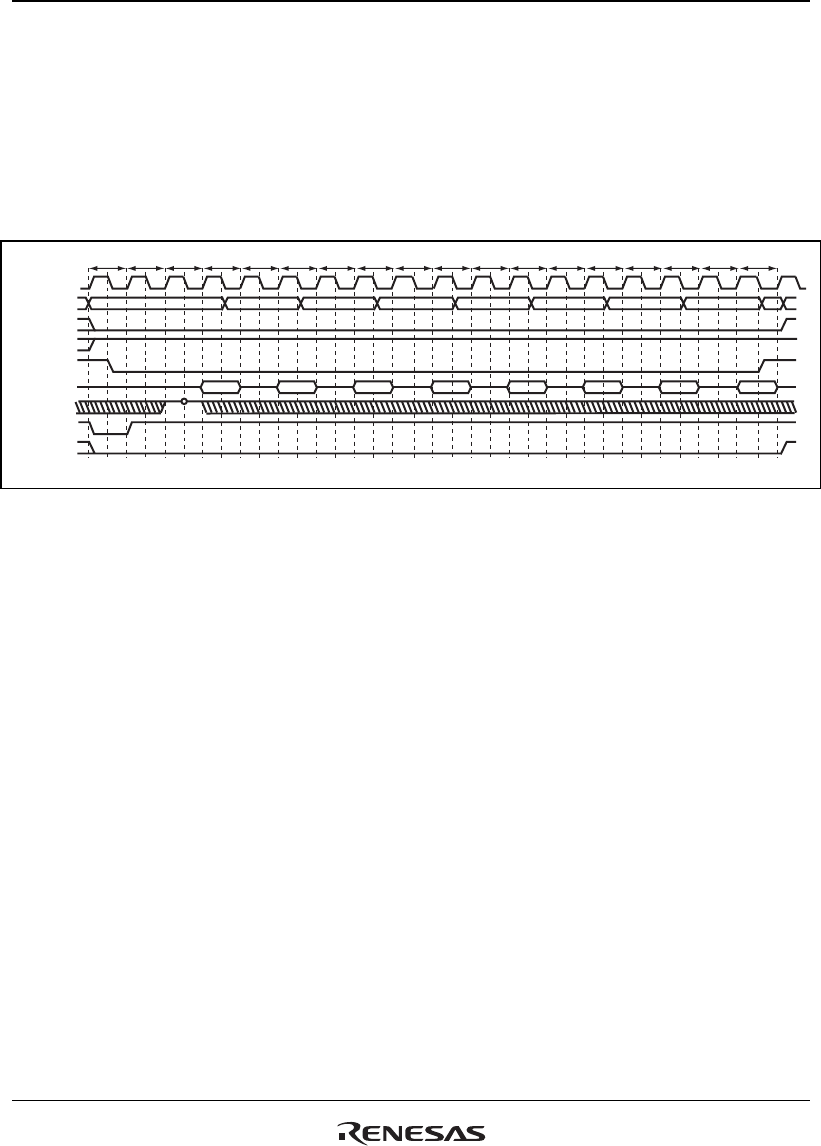
TwbT1 T2Tw T2BTw T2B Twb TwbT2B T2B Twb TwbT2B T2B Twb T2B Twb
Note: * The waveform for DACKn is when active low is specified.
CKIO
D31 to D0
A25 to A0
FRAME
CS6B
RD/WR
WAIT
BS
DACKn*
Figure 12.47 Burst ROM Access Timing (Clock Synchronous)
(Burst Length = 8, Wait Cycles Inserted in First Access = 2,
Wait Cycles Inserted in Second and Subsequent Accesses = 1)
12.5.11 Wait between Access Cycles
As the operating frequency of LSIs becomes higher, the off-operation of the data buffer often
collides with the next data access when the read operation from devices with slow access speed is
completed. As a result of these collisions, the reliability of the device is low and malfunctions may
occur. A function that avoids data collisions by inserting wait cycles between continuous access
cycles has been newly added.
The number of wait cycles between access cycles can be set by bits IWW2 to IWW0, IWRWD2 to
IWRWD0, IWRWS2 to IWRWS0, IWRRD2 to IWRRD0, and IWRRS2 to IWRRS 0 in the
CSnBCR register , and bit DMAIW2 to DMAIW0 and DMAIWA in CMNCR. The conditions for
setting the wait cycles between access cycles (idle cycles) are shown below.
1. Continuous accesses are write-read or write-write
2. Continuous accesses are read-write for different spaces
3. Continuous accesses are read-write for the same space
4. Continuous accesses are read-read for different spaces
5. Continuous accesses are read-read for the same space


















