Section 13 Direct Memory Access Controller (DMAC)
Rev. 4.00 Sep. 14, 2005 Page 433 of 982
REJ09B0023-0400
Address Modes:
1. Dual Address Mode
In the dual address mode, both the transfer source and destination are accessed (selected) by an
address. The source and destination can be located externally or internally.
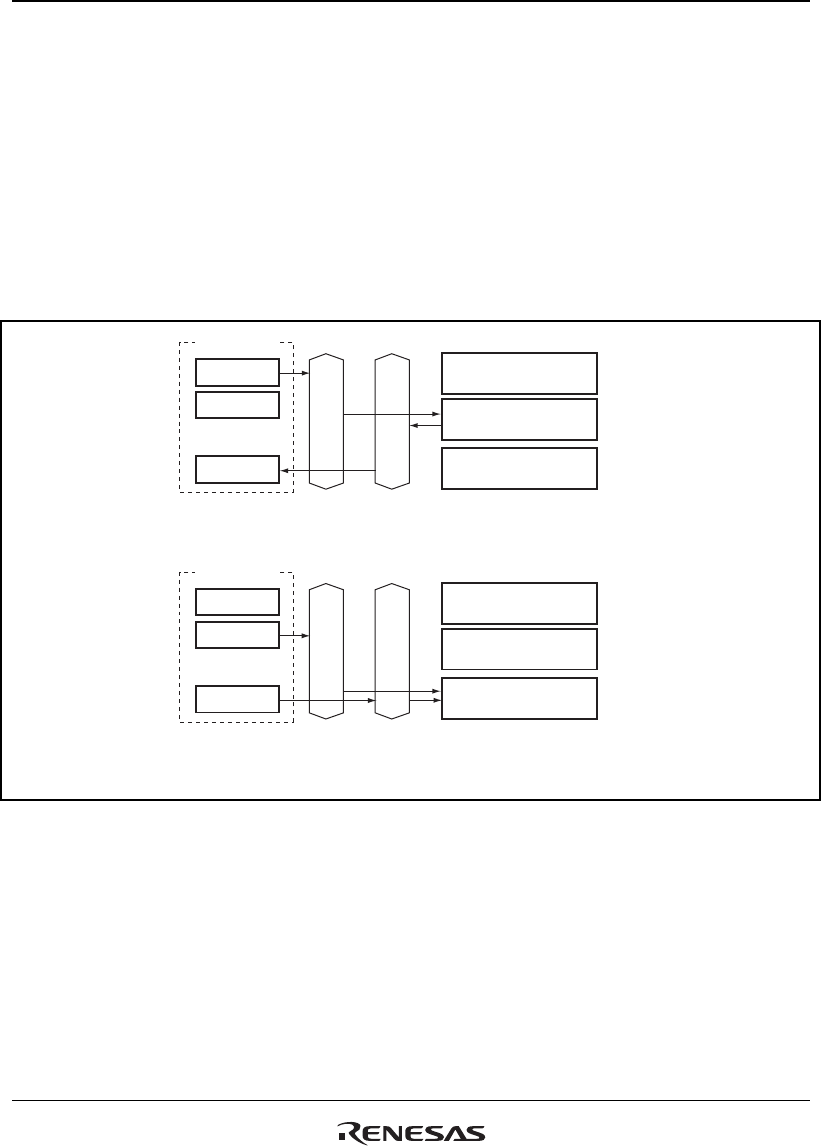
DMA transfer requires two bus cycles because data is read from the transfer source in a data
read cycle and written to the transfer destination in a data write cycle. At this time, transfer
data is temporarily stored in the DMAC. In the transfer between external memories as shown
in figure 13.5, data is read to the DMAC from one external memory in a data read cycle, and
then that data is written to the other external memory in a write cycle.
Data buffer
Address bus
Data bus
Address bus
Data bus
Memory
Transfer source
module
Transfer destination
module
Memory
Transfer source
module
Transfer destination
module
SAR
DAR
Data buffer
SAR
DAR
The SAR value is an address, data is read from the transfer source module,
and the data is tempolarily stored in the DMAC.
First bus cycle
Second bus cycle
The DAR value is an address and the value stored in the data buffer in the
DMAC is written to the transfer destination module.
DMAC
DMAC
Figure 13.5 Data Flow of Dual Address Mode
Auto request, external request, and on-chip peripheral module request are available for the
transfer request. DACK can be output in read cycle or write cycle in dual address mode. The
AM bit of the channel control register (CHCR) can specify whether the DACK is output in
read cycle or write cycle.


















