Section 19 Serial Communication Interface with FIFO (SCIF)
Rev. 4.00 Sep. 14, 2005 Page 732 of 982
REJ09B0023-0400
In serial reception, the SCIF operates as described below.
1. The SCIF monitors the transmission line, and if a 0 start bit is detected, performs internal
synchronization and starts reception.
2. The received data is stored in SCRSR in LSB-to-MSB order.
3. The parity bit and stop bit are received.
After receiving these bits, the SCIF carries out the following checks.
A. Stop bit check: The SCIF checks whether the stop bit is 1. If there are two stop bits, only
the first is checked.
B. The SCIF checks whether receive data can be transferred from the receive shift register
(SCRSR) to SCFRDR.
C. Overrun check: The SCIF checks that the ORER flag is 0, indicating that the overrun error
has not occurred.
D. Break check: The SCIF checks that the BRK flag is 0, indicating that the break state is not
set.
If all the above checks are passed, the receive data is stored in SCFRDR.
Note: When a parity error or a framing error occurs, reception is not suspended.
4. If the RIE bit in SCSCR is set to 1 when the RDF or DR flag changes to 1, a receive-FIFO-
data-full interrupt (RXI) request is generated. If the RIE bit or the REIE bit in SCSCR is set to
1 when the ER flag changes to 1, a receive-error interrupt (ERI) request is generated. If the
RIE bit or the REIE bit in SCSCR is set to 1 when the BRK or ORER flag changes to 1, a
break reception interrupt (BRI) request is generated.
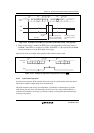
Figure 19.9 shows an example of the operation for reception.