985
Chapter 53 Fixed Mode-Reset Vector / BOOT-ROM
2.Check for Boot Conditions
2.2 Flash devices of MB91460 series (MB91F46x)
After the chip initialization and saving the RSRR (Reset Cause Register) to CPU register R4, there is a check for
boot conditions.
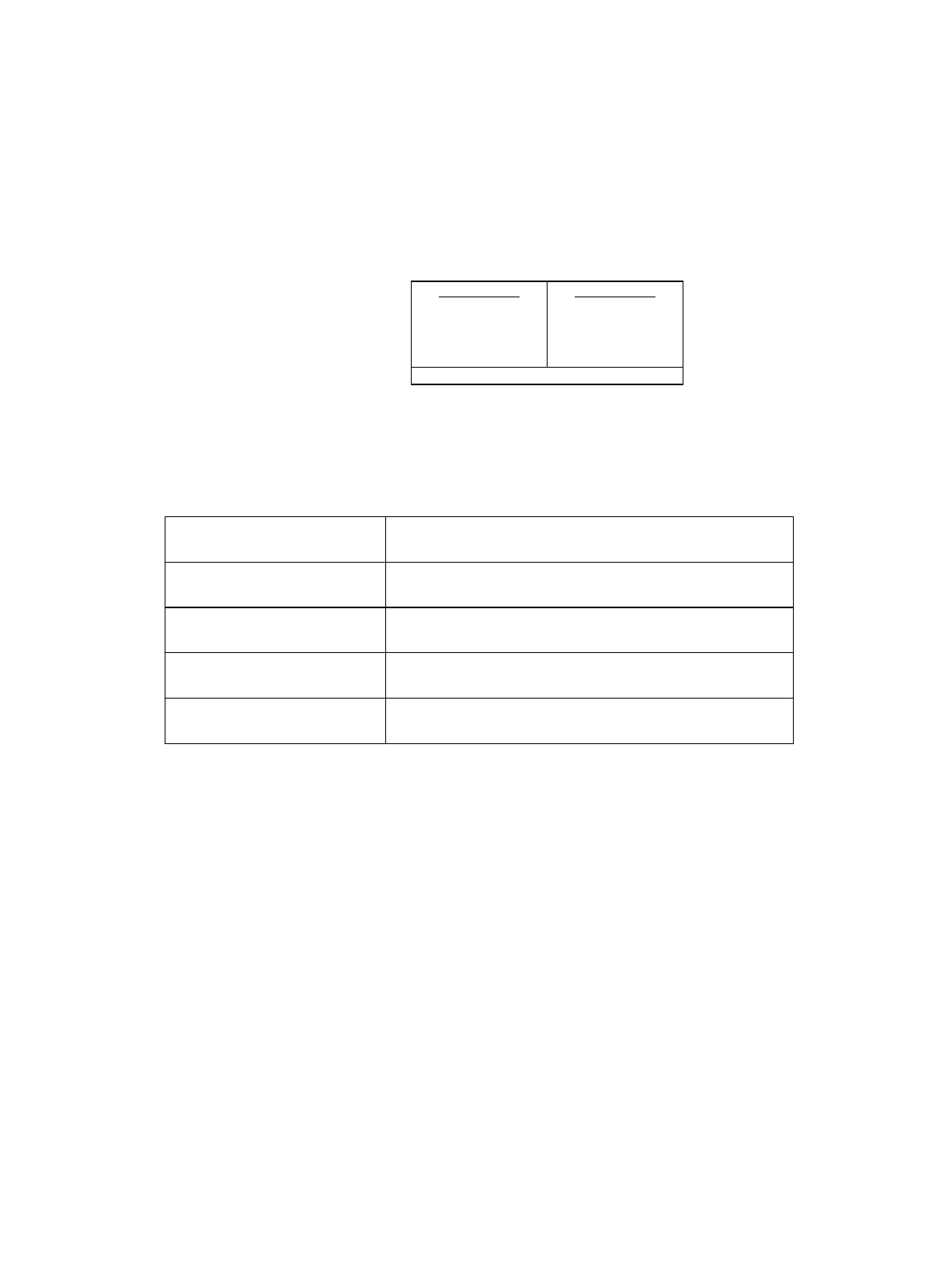
All Flash devices have two Boot Security Vectors (BSV1: 0x14:8004, BSV2: 0x14:800C). These vectors are
located in parallel sector to the Flash Security Vectors (FSV1, FSV2):
The Flash Security Vectors are used for configuring the protection mode of the flash memory sectors and do no
influence startup of Boot ROM. Refer to Chapter 55 Flash Security (Page No.1009).
At first, BSV1 is checked: if the data of this vector represents a valid address in the specified address range
(depending on Flash-ROM size), the Boot Security Vector itself becomes valid.
If BSV1 is valid, there will be an additional check before entering user program at the entry address given by BSV1
(1). Otherwise checks for entering the internal bootloader will be done (2).
The purpose of this feature is to disable the execution of the internal bootloader due to security reasons or to
minimize startup time of application. If the user sets BSV1 to a valid address range, this bootloader cannot be
entered any more.
(1) If the check for BSV1 is valid, the Magic Number, which should be located on the four bytes before the address
BSV1 points to, is compared to 0x000A897A. If the Magic Number matches this value, the user application is
entered at the address given by BSV1.
The Magic Number is used as flag for a valid user application, or especially for a user bootloader. If you want to re-
program this user bootloader, a second user bootloader, which handles the re-programming of the first user
bootloader, has to be located at the address BSV2 points to. If BSV2 does not point to a valid address range, then
application is started at default user program entry address 0x0F:4000. For more information on this bootloader
update strategy refer to chapter 5. Bootloader Update Strategy (Page No.990).
(2) If the check for BSV1 is not valid, the reset cause will be checked as second boot condition. Only if the reset
cause was an INIT reset (external INITX input, RSRR=0x80), the check for boot conditions will go on. Otherwise
Boot ROM is left and application is started at default user program entry address 0x0F:4000.
If the reset cause was an INIT reset, serial clock pin SCK4 is checked for an external clock signal. Therefore logic
level at this pin is monitored for about 1ms. If port level is constant, UART4 is initialized to asynchronous mode:
9600 baud, 8 data bits, 1 stop bit, no parity. If port level changes, UART4 is initialized to synchronous slave mode.
UART-reception is checked for about 100 ms. If during this time period the ASCII-character “V” (0x56) is received,
Sector SA4 Sector SA5
(8kB) (8kB)
……
0x14:8008 FSV2 BSV2
0x14:8000 FSV1 BSV1
64bit width
Device Valid Boot Security Vector address range
MB91F467DA 0x04:0000 – 0x14:FFFF
MB91F469GA 0x04:0000 – 0x24:FFFF
MB91F464AA
0x0A:0000 – 0x0F:FFFF
0x14:8000 – 0x14:FFFF
MB91F465KA
0x08:0000 – 0x0F:FFFF
0x14:8000 – 0x14:FFFF