549
Chapter 31 External Bus
4.Endian and Bus Access
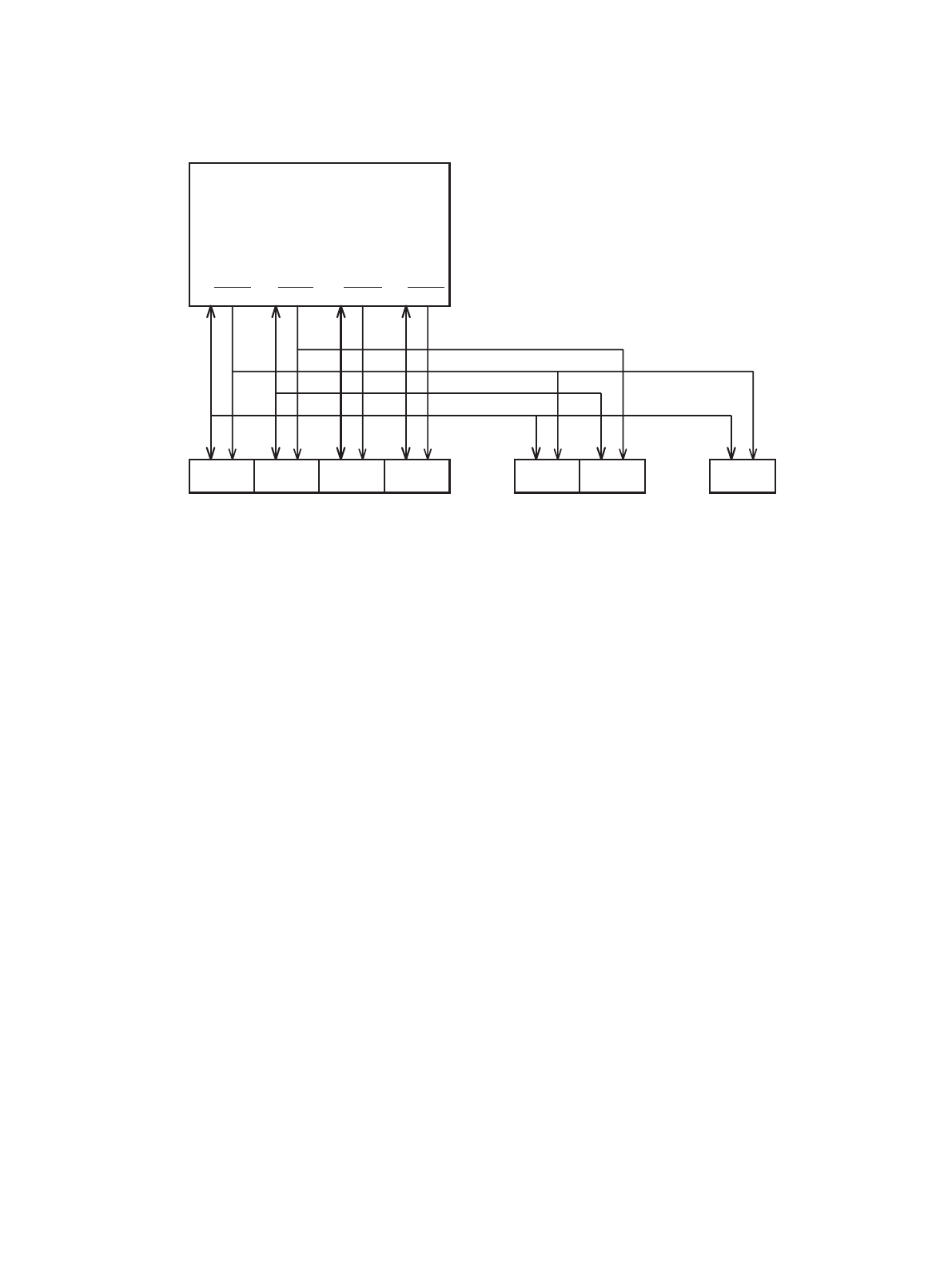
Figure 4-13 Example of Connecting the MB91460 Series to External Devices
4.2 Little Endian Bus Access
Little endian (LER) external bus access is performed for an area for which the little endian meth-
od is set.
Little endian bus access on the MB91460 series is implemented by using the bus access oper-
ation used for the big endian method. Basically, the order of output addresses and control signal
output are the same as for the big endian method and the byte locations on the data bus are
swapped in accordance with the bus width.
Note that, when a connection is made, the big endian area and the little endian area must be
kept physically separate.
■ Differences between Little Endian and Big Endian
The following explains the differences between little endian and big endian.
The order of addresses that are output is the same for little endian and big endian.
The data bus control signal used for 32/16/8-bit bus width is the same for little endian and big endian.
● Word access
The byte data on the MSB side for big endian address 00 becomes byte data on the LSB side when the little
endian method is used.
For a word address, the locations of all four bytes in the word are reversed:
00 -> 11, 01 -> 10, 10 -> 01, 11 -> 00
D31 D07 D00D00D15D00D16 D15 D08 D07D08 D07D24 D23
This LSI
D31
to
D24
D23
to
D16
D15
to
D08
D07
to
D00
00 01 10 11 0 1 0
* For 16/8-bit devices, use the data bus on
the MSB side of this LSI.
32-bit device
(low-order 2 bits of
the address 00 to 11)
*16-bit device
(low-order 1 bit of
the address 0/1)
*8-bit device
WR0 WR1 WR2
WR3


















