8
Chapter 1 Introduction
4.How to Use This Document
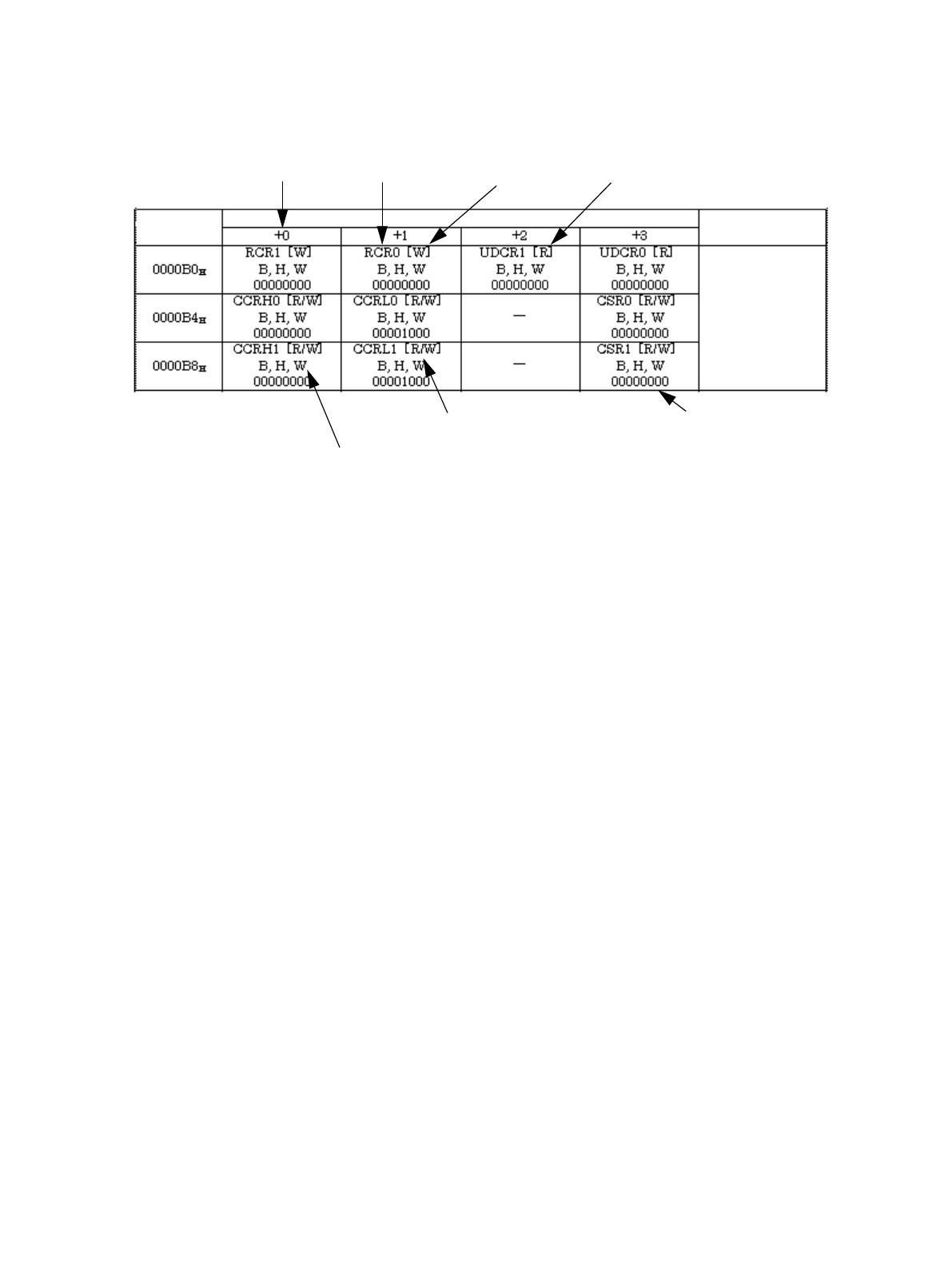
■ Access size and address position
There are three kinds of accesses such as Byte access, Half-word access and Word access. However, note
that some registers have restricted access. For more information, see “3.2. I/O Map (Page No.24)” or “Detail
Description of Register” in each chapter.
B,H,W : Byte access, Half-word access, and Wordaccess are allowed.
B : Byte access (Be sure to access by Byte.)
H : Half-word access (Be sure to access by Half-word.)
W : Word access (Be sure to access by Word.)
B, H : Byte access, Half-word access only (Word access is not allowed.)
H,W : Half-word access, Word access only (Byte access is not allowed.)
Reference
The following describes address position to access.
• In Word access, address becomes multiple of 4. (Lowest order 2 bits mandatorily become “00”.)
• In Half-word access, address becomes multiple of 2. (Lowest order 1 bit mandatorily becomes “0”.)
• In Byte access, address will not be changed.
Therefore, for example, make RCR0 register to use Half-word access,
For address 0B0H, RCR1+RCR0 register is accessed.
(When address offset is +1 and +2, (Example: RCR0+UDCR1) Half-word access is not allowed.)
Offset Register name Write-only Read-only
Byte access, Half-word access, and Word access are allowed.
Read/write
Initial value
Address offset value/Register name
Address
Up/down counter
0, 1
Block


















