333
Chapter 26 DMA Controller
1.Overview of the DMA Controller (DMAC)
Chapter 26 DMA Controller
1. Overview of the DMA Controller (DMAC)
The DMA controller (DMAC) is a module that implements DMA (Direct Memory Access) transfer
on FR family devices. When this module is used to control DMA transfer, various kinds of data
can be transferred at high speed by bypassing the CPU, enhancing system performance.
■ Hardware Configuration
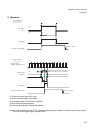
The DMA controller (DMAC) consists mainly of the following blocks:
Five independent DMA channels
• 5-channel independent access control circuit
• 32-bit address registers (reload specifiable, two registers for each channel)
• 16-bit transfer count register (reload specifiable, one register for each channel)
• 4-bit block count register (one for each channel)
• Up to 128 internal transfer request sources
• External transfer request input pins: DREQ0, DREQ1, DREQ2, DREQ3 (for ch0-3 only)
• External transfer request acceptance output pins: DACK0, DACK1, DACK2, DACK3 (for ch0-3 only)
• DMA end output pins: DEOP0, DEOP1, DEOP2, DEOP3 (for ch0-3 only)
• Fly-by transfer (memory to I/O and I/O to memory) (for ch0-3 only)
• 2-cycle transfer
■ Main Functions
The following are the main functions related to data transfer by the DMA controller (DMAC):
Data can be transferred independently over multiple channels (5 channels)
● Priority (ch.0>ch.1>ch.2>ch.3>ch.4)
● The order can be rotated between ch.0 and ch.1.
● DMAC start sources
• External dedicated pin input (edge detection/level detection for ch0-3 only)
• Built-in peripheral requests (shared interrupt requests, including external interrupts)
• Software request (register write)
● Transfer mode
• Demand transfer, burst transfer, step transfer, and block transfer
• Addressing mode: 32-bit full addressing (increment/decrement/fixed)
The address increment/decrement range is from -255 to +255.
• Data types: Byte, halfword, and word length
• Single shot/reload selectable