282
Chapter 20 Software Watchdog Timer
8.Caution
8. Caution
• Although the watchdog interval time corresponds to the one twice as long as the watchdog 1-bit counter, the
watchdog timer clear operation only clears the 1-bit counter used for detecting the watchdog. As a result, the
time margin to clear the watchdog timer is different from the interval time.
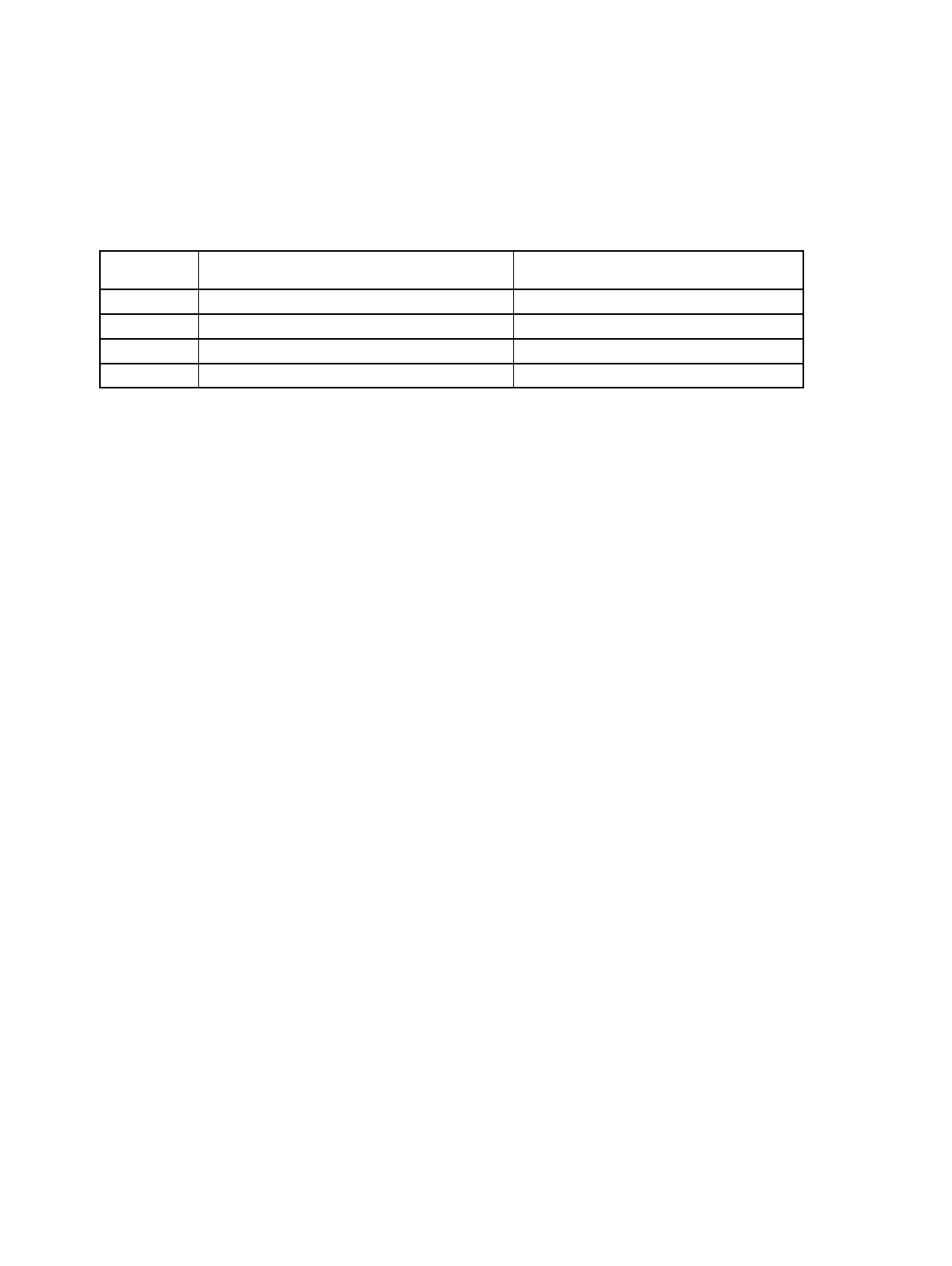
Watchdog interval time selection
• The watchdog timer is started once data is written in the watchdog timer control register.
• The watchdog timer control register is also the reset cause register and the status (INIT, HSTB, WDOG,
ERST, SRST and LINIT) is set to “0” when it is read.
• The watchdog reset holds the oscillation stability wait time.
(Refer to “Chapter 18 Timebase Counter (Page No.249)”.)
• The watchdog reset from the main RUN or the sub-RUN where the main clock oscillation is in process
cannot have the oscillation stability wait time because the main clock is oscillating.
• Refer to “Chapter 19 Timebase Timer (Page No.263)” for the method of clearing the timebase counter that is the
count source for the watchdog timer.
• Clearing the timebase counter causes the watchdog reset timing to be postponed once.
WT1-WT0
Time margin to clear the watchdog timer Interval time during which the watchdog
reset is generated
00
Φ × 2
20
(Initial value) Φ × 2
20
to Φ × 2
21
01
Φ × 2
22
Φ × 2
22
to Φ × 2
23
10
Φ × 2
24
Φ × 2
24
to Φ × 2
25
11
Φ × 2
26
Φ × 2
26
to Φ × 2
27


















